|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| benchmarks | ||
| coati | ||
| conversation_template | ||
| examples | ||
| tests | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| pytest.ini | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| setup.py | ||
| version.txt | ||
README.md

ColossalChat
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- What is ColossalChat?
- Online demo
- Install
- Introduction
- Supervised datasets collection
- RLHF Training Stage1 - Supervised instructs tuning
- RLHF Training Stage2 - Training reward model
- RLHF Training Stage3 - Training model with reinforcement learning by human feedback
- Alternative Option for RLHF: GRPO
- Alternative Option For RLHF: DPO
- Alternative Option For RLHF: SimPO
- Alternative Option For RLHF: ORPO
- Alternative Option For RLHF: KTO
- SFT for DeepSeek V3/R1
- Inference Quantization and Serving - After Training
- Invitation to open-source contribution
- Quick Preview
- Authors
- Citations
- Licenses
What is ColossalChat?
ColossalChat is a project to implement LLM with RLHF, powered by the Colossal-AI.
Coati stands for ColossalAI Talking Intelligence. It is the name for the module implemented in this project and is also the name of the large language model developed by the ColossalChat project.
The Coati package provides a unified large language model framework that has implemented the following functions
- Supports comprehensive large-model training acceleration capabilities for ColossalAI, without requiring knowledge of complex distributed training algorithms
- Supervised datasets collection
- Supervised instructions fine-tuning
- Training reward model
- Reinforcement learning with human feedback
- Perfectly integrated with the Hugging Face ecosystem, a high degree of model customization
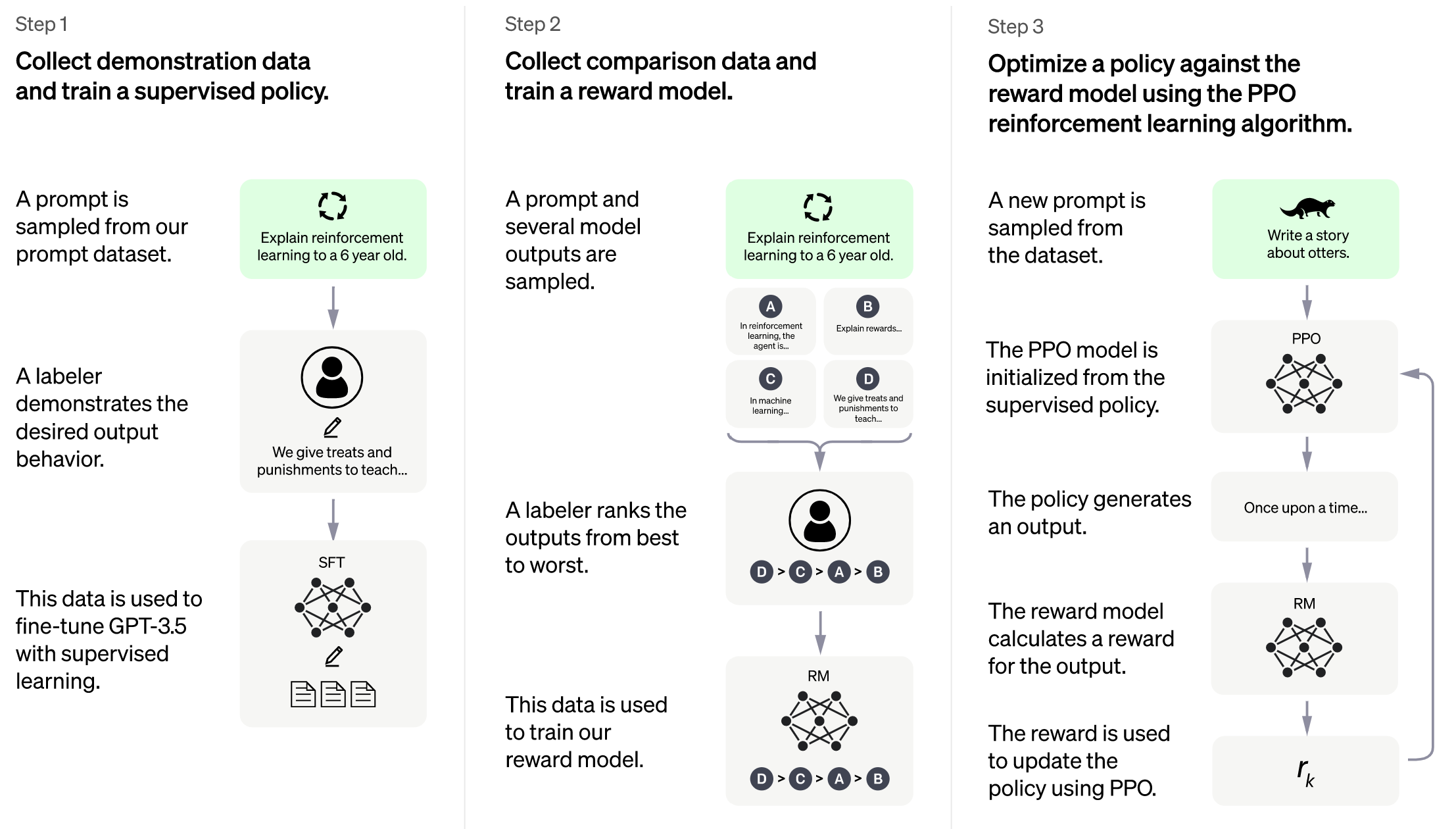
Image source: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
As Colossal-AI is undergoing some major updates, this project will be actively maintained to stay in line with the Colossal-AI project.
More details can be found in the latest news.
- [2023/03] ColossalChat: An Open-Source Solution for Cloning ChatGPT With a Complete RLHF Pipeline
- [2023/02] Open Source Solution Replicates ChatGPT Training Process! Ready to go with only 1.6GB GPU Memory
Online demo
ColossalChat: An open-source solution for cloning ChatGPT with a complete RLHF pipeline. [code] [blog] [demo] [tutorial]
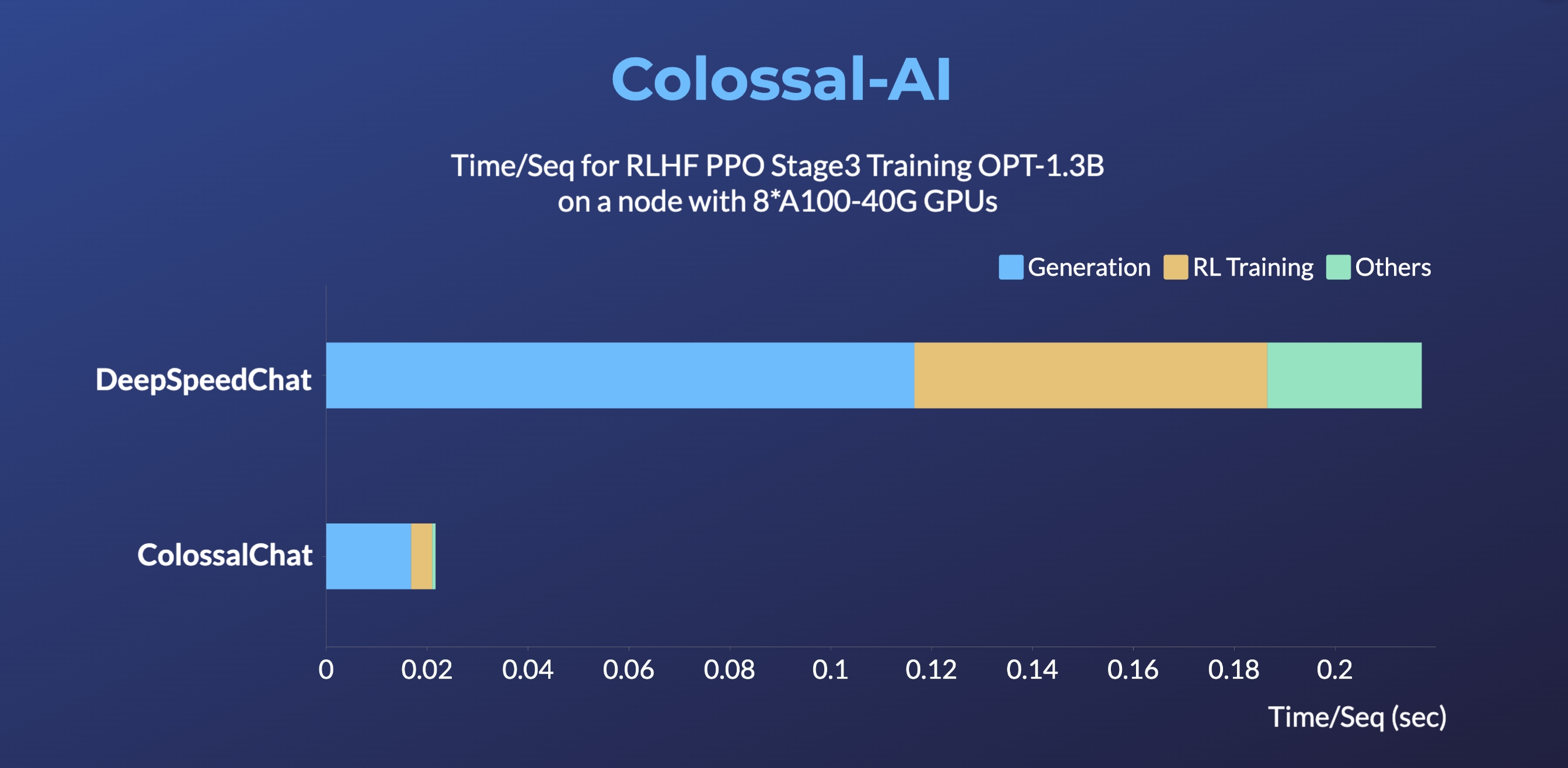
DeepSpeedChat performance comes from its blog on 2023 April 12, ColossalChat performance can be reproduced on an AWS p4d.24xlarge node with 8 A100-40G GPUs with the following command:
torchrun --standalone --nproc_per_node 8 benchmark_opt_lora_dummy.py --num_collect_steps 1 --use_kernels --strategy colossalai_zero2 --experience_batch_size 64 --train_batch_size 32
Install
Install the Environment
# Create new environment
conda create -n colossal-chat python=3.10.9 (>=3.8.7)
conda activate colossal-chat
# Clone ColossalAI
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI.git
# Install ColossalAI, make sure you have torch installed before using BUILD_EXT=1.
cd $COLOSSAL_AI_ROOT
BUILD_EXT=1 pip install .
# Install ColossalChat
cd $COLOSSAL_AI_ROOT/applications/ColossalChat
pip install .
Introduction
RLHF Training Stage1 - Supervised Instructs Tuning
Stage1 is supervised instructs fine-tuning (SFT). This step is a crucial part of the RLHF training process, as it involves training a machine learning model using human-provided instructions to learn the initial behavior for the task at hand. More details can be found in example guideline.
RLHF Training Stage2 - Training Reward Model
Stage2 trains a reward model, which obtains corresponding scores by manually ranking different outputs for the same prompt and supervises the training of the reward model.
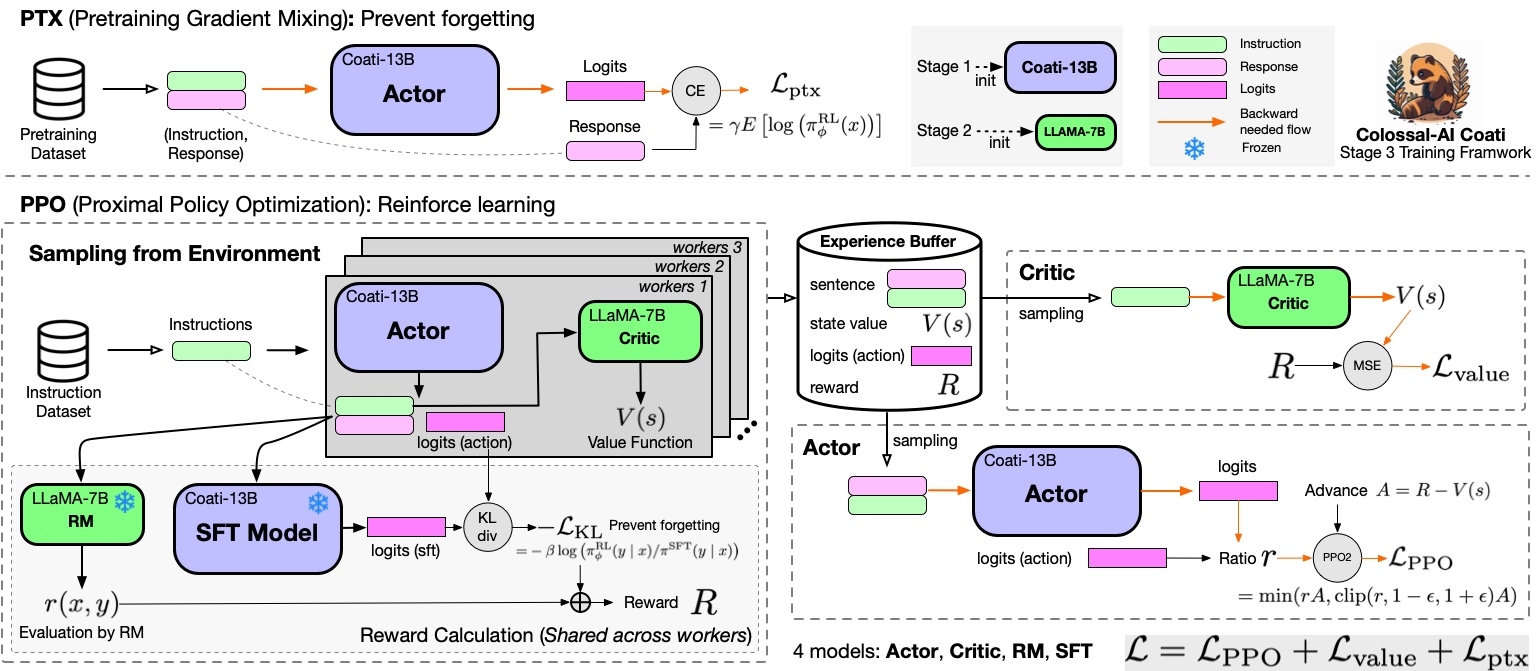
RLHF Training Stage3 - Proximal Policy Optimization
In stage3 we will use reinforcement learning algorithm--- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), which is the most complex part of the training process:
Alternative Option For RLHF: Direct Preference Optimization (DPO)
For those seeking an alternative to Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) presents a compelling option. DPO, as detailed in this paper, DPO offers an low-cost way to perform RLHF and usually request less computation resources compares to PPO. Read this README for more information.
Alternative Option For RLHF: Simple Preference Optimization (SimPO)
Simple Preference Optimization (SimPO) from this paper is similar to DPO but it abandons the use of the reference model, which makes the training more efficient. It also adds a reward shaping term called target reward margin to enhance training stability. It also use length normalization to better align with the inference process. Read this README for more information.
Alternative Option For RLHF: Odds Ratio Preference Optimization (ORPO)
Odds Ratio Preference Optimization (ORPO) from this paper is a reference model free alignment method that use a mixture of SFT loss and a reinforcement leanring loss calculated based on odds-ratio-based implicit reward to makes the training more efficient and stable. Read this README for more information.
Alternative Option For RLHF: Kahneman-Tversky Optimization (KTO)
We support the method introduced in the paper KTO:Model Alignment as Prospect Theoretic Optimization (KTO). Which is a aligment method that directly maximize "human utility" of generation results. Read this README for more information.
Alternative Option For RLHF: Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)
We support the main algorithm used to train DeepSeek R1 model, a variant of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), that enhances mathematical reasoning abilities while concurrently optimizing the memory usage of PPO. Read this README for more information.
SFT for DeepSeek V3
We support fine-tuning DeepSeek V3/R1 model with LoRA. Read this README for more information.
Inference Quantization and Serving - After Training
We provide an online inference server and a benchmark. We aim to run inference on single GPU, so quantization is essential when using large models.
We support 8-bit quantization (RTN), 4-bit quantization (GPTQ), and FP16 inference.
Online inference server scripts can help you deploy your own services.
For more details, see inference/.
Invitation to open-source contribution
Referring to the successful attempts of BLOOM and Stable Diffusion, any and all developers and partners with computing powers, datasets, models are welcome to join and build the Colossal-AI community, making efforts towards the era of big AI models from the starting point of replicating ChatGPT!
You may contact us or participate in the following ways:
- Leaving a Star ⭐ to show your like and support. Thanks!
- Posting an issue, or submitting a PR on GitHub follow the guideline in Contributing.
- Join the Colossal-AI community on Slack, and WeChat(微信) to share your ideas.
- Send your official proposal to email contact@hpcaitech.com
Thanks so much to all of our amazing contributors!
Quick Preview
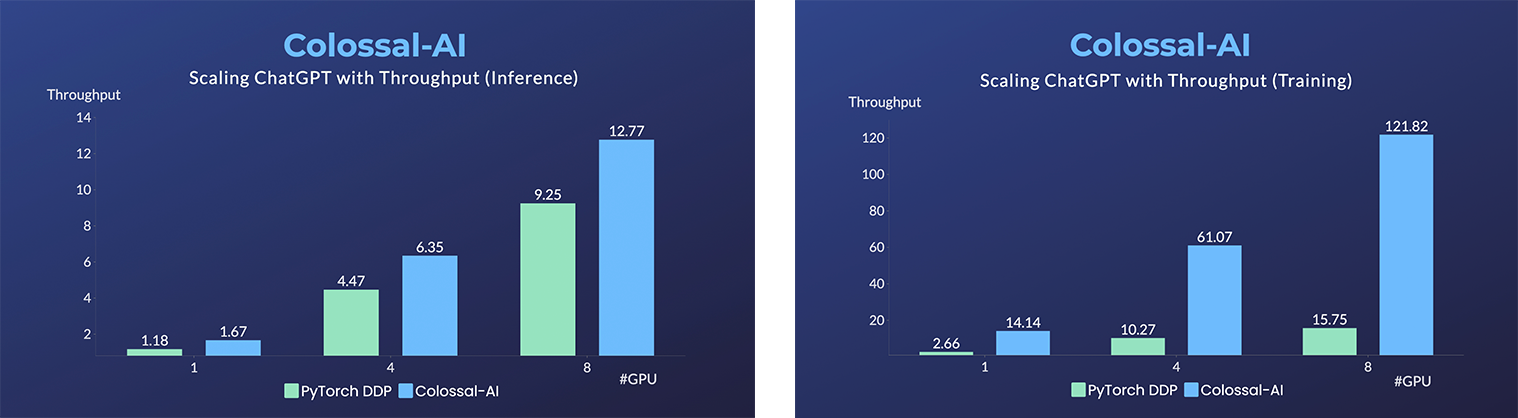
- Up to 7.73 times faster for single server training and 1.42 times faster for single-GPU inference
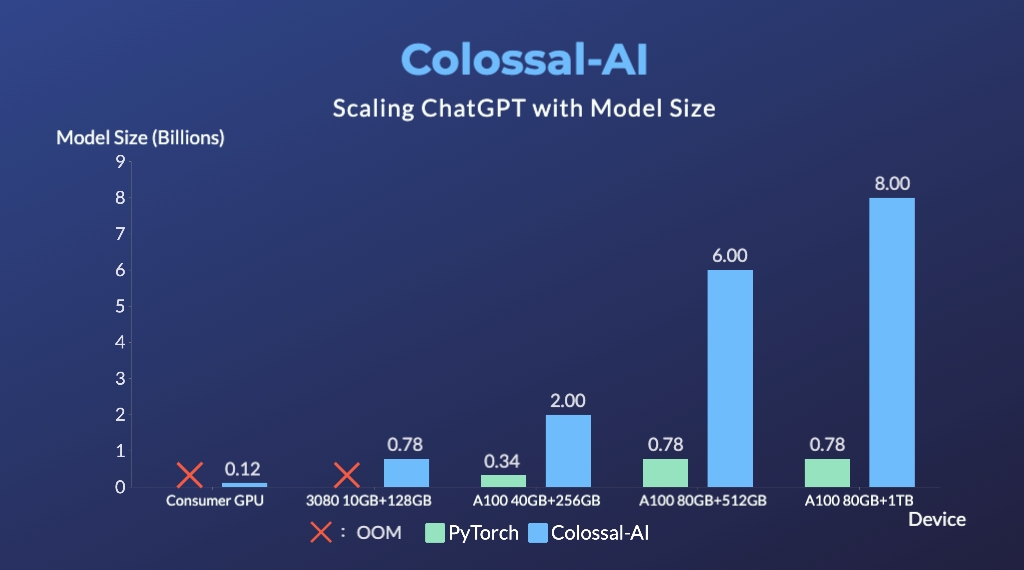
- Up to 10.3x growth in model capacity on one GPU
- A mini demo training process requires only 1.62GB of GPU memory (any consumer-grade GPU)
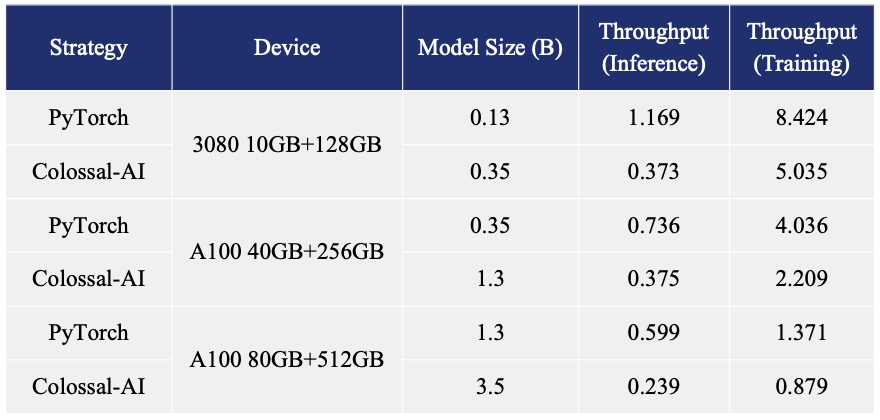
- Increase the capacity of the fine-tuning model by up to 3.7 times on a single GPU
- Keep in a sufficiently high running speed
Authors
Coati is developed by ColossalAI Team:
- ver217 Leading the project while contributing to the main framework (System Lead).
- Tong Li Leading the project while contributing to the main framework (Algorithm Lead).
- Anbang Ye Contributing to the refactored PPO version with updated acceleration framework. Add support for DPO, SimPO, ORPO.
- FrankLeeeee Providing ML infra support and also taking charge of both front-end and back-end development.
- htzhou Contributing to the algorithm and development for RM and PPO training.
- Fazzie Contributing to the algorithm and development for SFT.
- ofey404 Contributing to both front-end and back-end development.
- Wenhao Chen Contributing to subsequent code enhancements and performance improvements.
The PhD student from (HPC-AI) Lab also contributed a lot to this project.
We also appreciate the valuable suggestions provided by Jian Hu regarding the convergence of the PPO algorithm.
Citations
@article{Hu2021LoRALA,
title = {LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models},
author = {Edward J. Hu and Yelong Shen and Phillip Wallis and Zeyuan Allen-Zhu and Yuanzhi Li and Shean Wang and Weizhu Chen},
journal = {ArXiv},
year = {2021},
volume = {abs/2106.09685}
}
@article{ouyang2022training,
title={Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback},
author={Ouyang, Long and Wu, Jeff and Jiang, Xu and Almeida, Diogo and Wainwright, Carroll L and Mishkin, Pamela and Zhang, Chong and Agarwal, Sandhini and Slama, Katarina and Ray, Alex and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.02155},
year={2022}
}
@article{touvron2023llama,
title={LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models},
author={Touvron, Hugo and Lavril, Thibaut and Izacard, Gautier and Martinet, Xavier and Lachaux, Marie-Anne and Lacroix, Timoth{\'e}e and Rozi{\`e}re, Baptiste and Goyal, Naman and Hambro, Eric and Azhar, Faisal and Rodriguez, Aurelien and Joulin, Armand and Grave, Edouard and Lample, Guillaume},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971},
year={2023}
}
@misc{alpaca,
author = {Rohan Taori and Ishaan Gulrajani and Tianyi Zhang and Yann Dubois and Xuechen Li and Carlos Guestrin and Percy Liang and Tatsunori B. Hashimoto },
title = {Stanford Alpaca: An Instruction-following LLaMA model},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca}},
}
@misc{instructionwild,
author = {Fuzhao Xue and Zangwei Zheng and Yang You },
title = {Instruction in the Wild: A User-based Instruction Dataset},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/XueFuzhao/InstructionWild}},
}
@misc{meng2024simposimplepreferenceoptimization,
title={SimPO: Simple Preference Optimization with a Reference-Free Reward},
author={Yu Meng and Mengzhou Xia and Danqi Chen},
year={2024},
eprint={2405.14734},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.14734},
}
@misc{rafailov2023directpreferenceoptimizationlanguage,
title={Direct Preference Optimization: Your Language Model is Secretly a Reward Model},
author={Rafael Rafailov and Archit Sharma and Eric Mitchell and Stefano Ermon and Christopher D. Manning and Chelsea Finn},
year={2023},
eprint={2305.18290},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.18290},
}
@misc{hong2024orpomonolithicpreferenceoptimization,
title={ORPO: Monolithic Preference Optimization without Reference Model},
author={Jiwoo Hong and Noah Lee and James Thorne},
year={2024},
eprint={2403.07691},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.07691},
}
@misc{shao2024deepseekmathpushinglimitsmathematical,
title={DeepSeekMath: Pushing the Limits of Mathematical Reasoning in Open Language Models},
author={Zhihong Shao and Peiyi Wang and Qihao Zhu and Runxin Xu and Junxiao Song and Xiao Bi and Haowei Zhang and Mingchuan Zhang and Y. K. Li and Y. Wu and Daya Guo},
year={2024},
eprint={2402.03300},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.03300},
}
@misc{logic-rl,
author = {Tian Xie and Qingnan Ren and Yuqian Hong and Zitian Gao and Haoming Luo},
title = {Logic-RL},
howpublished = {https://github.com/Unakar/Logic-RL},
note = {Accessed: 2025-02-03},
year = {2025}
}
Licenses
Coati is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.