13 KiB
ColoDiffusion: Stable Diffusion with Colossal-AI
Acceleration of AIGC (AI-Generated Content) models such as Stable Diffusion v1 and Stable Diffusion v2.
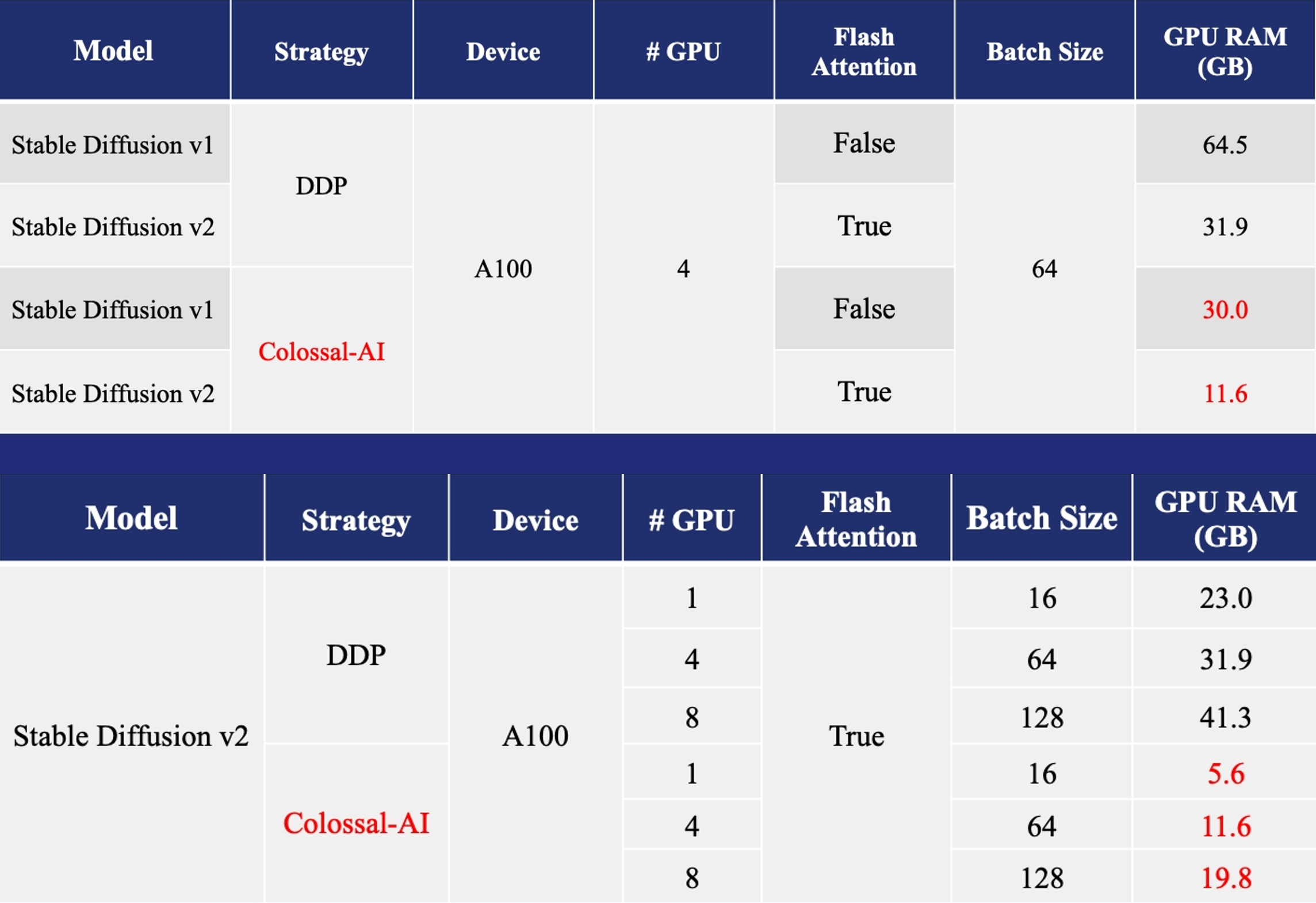
- Training: Reduce Stable Diffusion memory consumption by up to 5.6x and hardware cost by up to 46x (from A100 to RTX3060).

- DreamBooth Fine-tuning: Personalize your model using just 3-5 images of the desired subject.

- Inference: Reduce inference GPU memory consumption by 2.5x.
More details can be found in our blog of Stable Diffusion v1 and blog of Stable Diffusion v2.
Roadmap
This project is in rapid development.
- Train a stable diffusion model v1/v2 from scatch
- Finetune a pretrained Stable diffusion v1 model
- Inference a pretrained model using PyTorch
- Finetune a pretrained Stable diffusion v2 model
- Inference a pretrained model using TensoRT
Installation
Option #1: Install from source
Step 1: Requirements
To begin with, make sure your operating system has the cuda version suitable for this exciting training session, which is cuda11.6/11.8. For your convience, we have set up the rest of packages here. You can create and activate a suitable conda environment named ldm :
conda env create -f environment.yaml
conda activate ldm
You can also update an existing latent diffusion environment by running:
conda install pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch
pip install transformers diffusers invisible-watermark
Step 2: Install Colossal-AI From Our Official Website
You can install the latest version (0.2.7) from our official website or from source. Notice that the suitable version for this training is colossalai(0.2.5), which stands for torch(1.12.1).
Download suggested version for this training
pip install colossalai==0.2.5
Download the latest version from pip for latest torch version
pip install colossalai
From source:
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI.git
cd ColossalAI
# install colossalai
CUDA_EXT=1 pip install .
Step 3: Accelerate with flash attention by xformers (Optional)
Notice that xformers will accelerate the training process at the cost of extra disk space. The suitable version of xformers for this training process is 0.0.12, which can be downloaded directly via pip. For more release versions, feel free to check its official website: XFormers
pip install xformers==0.0.12
Option #2: Use Docker
To use the stable diffusion Docker image, you can either build using the provided the Dockerfile or pull a Docker image from our Docker hub.
# 1. build from dockerfile
cd ColossalAI/examples/images/diffusion/docker
docker build -t hpcaitech/diffusion:0.2.0 .
# 2. pull from our docker hub
docker pull hpcaitech/diffusion:0.2.0
Once you have the image ready, you can launch the image with the following command
########################
# On Your Host Machine #
########################
# make sure you start your image in the repository root directory
cd ColossalAI
# run the docker container
docker run --rm \
-it --gpus all \
-v $PWD:/workspace \
-v <your-data-dir>:/data/scratch \
-v <hf-cache-dir>:/root/.cache/huggingface \
hpcaitech/diffusion:0.2.0 \
/bin/bash
########################
# Inside a Container #
########################
# Once you have entered the docker container, go to the stable diffusion directory for training
cd examples/images/diffusion/
# Download the model checkpoint from pretrained (See the following steps)
# Set up your configuration the "train_colossalai.sh" (See the following steps)
# start training with colossalai
bash train_colossalai.sh
It is important for you to configure your volume mapping in order to get the best training experience.
- Mandatory, mount your prepared data to
/data/scratchvia-v <your-data-dir>:/data/scratch, where you need to replace<your-data-dir>with the actual data path on your machine. Notice that within docker we need to transform the Windows path to a Linux one, e.g.C:\User\Desktopinto/mnt/c/User/Desktop. - Recommended, store the downloaded model weights to your host machine instead of the container directory via
-v <hf-cache-dir>:/root/.cache/huggingface, where you need to replace the<hf-cache-dir>with the actual path. In this way, you don't have to repeatedly download the pretrained weights for everydocker run. - Optional, if you encounter any problem stating that shared memory is insufficient inside container, please add
-v /dev/shm:/dev/shmto yourdocker runcommand.
Download the model checkpoint from pretrained
stable-diffusion-v2-base (Recommended)
wget https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-base/resolve/main/512-base-ema.ckpt
stable-diffusion-v1-4
git lfs install
git clone https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4
stable-diffusion-v1-5 from runway
git lfs install
git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
Dataset
The dataSet is from LAION-5B, the subset of LAION,
you should the change the data.file_path in the config/train_colossalai.yaml
Training
We provide the script train_colossalai.sh to run the training task with colossalai. Meanwhile, we have enlightened other training process such as DDP model in PyTorch. You can also use train_ddp.sh to run the training task with ddp to compare the corresponding performance.
In train_colossalai.sh the main command is
python main.py --logdir /tmp/ --train --base configs/train_colossalai.yaml --ckpt 512-base-ema.ckpt
- You can change the
--logdirto decide where to save the log information and the last checkpoint.- You will find your ckpt in
logdir/checkpointsorlogdir/diff_tb/version_0/checkpoints - You will find your train config yaml in
logdir/configs
- You will find your ckpt in
- You can add the
--ckptif you want to load the pretrained model, for example512-base-ema.ckpt - You can change the
--baseto specify the path of config yaml
Training config
You can change the training config in the yaml file
- devices: device number used for training, default = 8
- max_epochs: max training epochs, default = 2
- precision: the precision type used in training, default = 16 (fp16), you must use fp16 if you want to apply colossalai
- placement_policy: the training strategy supported by Colossal AI, default = 'cuda', which refers to loading all the parameters into cuda memory. On the other hand, 'cpu' refers to 'cpu offload' strategy while 'auto' enables 'Gemini', both featured by Colossal AI.
- more information about the configuration of ColossalAIStrategy can be found here
Finetune Example
Training on Teyvat Datasets
We provide the finetuning example on Teyvat dataset, which is create by BLIP generated captions.
You can run by config configs/Teyvat/train_colossalai_teyvat.yaml
python main.py --logdir /tmp/ -t -b configs/Teyvat/train_colossalai_teyvat.yaml
Inference
You can get your training last.ckpt and train config.yaml in your --logdir, and run by
python scripts/txt2img.py --prompt "a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse" --plms
--outdir ./output \
--ckpt path/to/logdir/checkpoints/last.ckpt \
--config /path/to/logdir/configs/project.yaml \
usage: txt2img.py [-h] [--prompt [PROMPT]] [--outdir [OUTDIR]] [--skip_grid] [--skip_save] [--ddim_steps DDIM_STEPS] [--plms] [--laion400m] [--fixed_code] [--ddim_eta DDIM_ETA]
[--n_iter N_ITER] [--H H] [--W W] [--C C] [--f F] [--n_samples N_SAMPLES] [--n_rows N_ROWS] [--scale SCALE] [--from-file FROM_FILE] [--config CONFIG] [--ckpt CKPT]
[--seed SEED] [--precision {full,autocast}]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--prompt [PROMPT] the prompt to render
--outdir [OUTDIR] dir to write results to
--skip_grid do not save a grid, only individual samples. Helpful when evaluating lots of samples
--skip_save do not save individual samples. For speed measurements.
--ddim_steps DDIM_STEPS
number of ddim sampling steps
--plms use plms sampling
--laion400m uses the LAION400M model
--fixed_code if enabled, uses the same starting code across samples
--ddim_eta DDIM_ETA ddim eta (eta=0.0 corresponds to deterministic sampling
--n_iter N_ITER sample this often
--H H image height, in pixel space
--W W image width, in pixel space
--C C latent channels
--f F downsampling factor
--n_samples N_SAMPLES
how many samples to produce for each given prompt. A.k.a. batch size
--n_rows N_ROWS rows in the grid (default: n_samples)
--scale SCALE unconditional guidance scale: eps = eps(x, empty) + scale * (eps(x, cond) - eps(x, empty))
--from-file FROM_FILE
if specified, load prompts from this file
--config CONFIG path to config which constructs model
--ckpt CKPT path to checkpoint of model
--seed SEED the seed (for reproducible sampling)
--use_int8 whether to use quantization method
--precision {full,autocast}
evaluate at this precision
Invitation to open-source contribution
Referring to the successful attempts of BLOOM and Stable Diffusion, any and all developers and partners with computing powers, datasets, models are welcome to join and build the Colossal-AI community, making efforts towards the era of big AI models!
You may contact us or participate in the following ways:
- Leaving a Star ⭐ to show your like and support. Thanks!
- Posting an issue, or submitting a PR on GitHub follow the guideline in Contributing.
- Join the Colossal-AI community on Slack, and WeChat(微信) to share your ideas.
- Send your official proposal to email contact@hpcaitech.com
Thanks so much to all of our amazing contributors!
Comments
-
Our codebase for the diffusion models builds heavily on OpenAI's ADM codebase , lucidrains, Stable Diffusion, Lightning and Hugging Face. Thanks for open-sourcing!
-
The implementation of the transformer encoder is from x-transformers by lucidrains.
-
The implementation of flash attention is from HazyResearch.
BibTeX
@article{bian2021colossal,
title={Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training},
author={Bian, Zhengda and Liu, Hongxin and Wang, Boxiang and Huang, Haichen and Li, Yongbin and Wang, Chuanrui and Cui, Fan and You, Yang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.14883},
year={2021}
}
@misc{rombach2021highresolution,
title={High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models},
author={Robin Rombach and Andreas Blattmann and Dominik Lorenz and Patrick Esser and Björn Ommer},
year={2021},
eprint={2112.10752},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
@article{dao2022flashattention,
title={FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness},
author={Dao, Tri and Fu, Daniel Y. and Ermon, Stefano and Rudra, Atri and R{\'e}, Christopher},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.14135},
year={2022}
}