16 KiB
Examples
Table of Contents
- Examples
Install requirements
pip install -r requirements.txt
Supervised datasets collection
We collected 104K bilingual dataset of Chinese and English, and you can find the datasets in this repo InstructionWild.
The following pic shows how we collected the data.
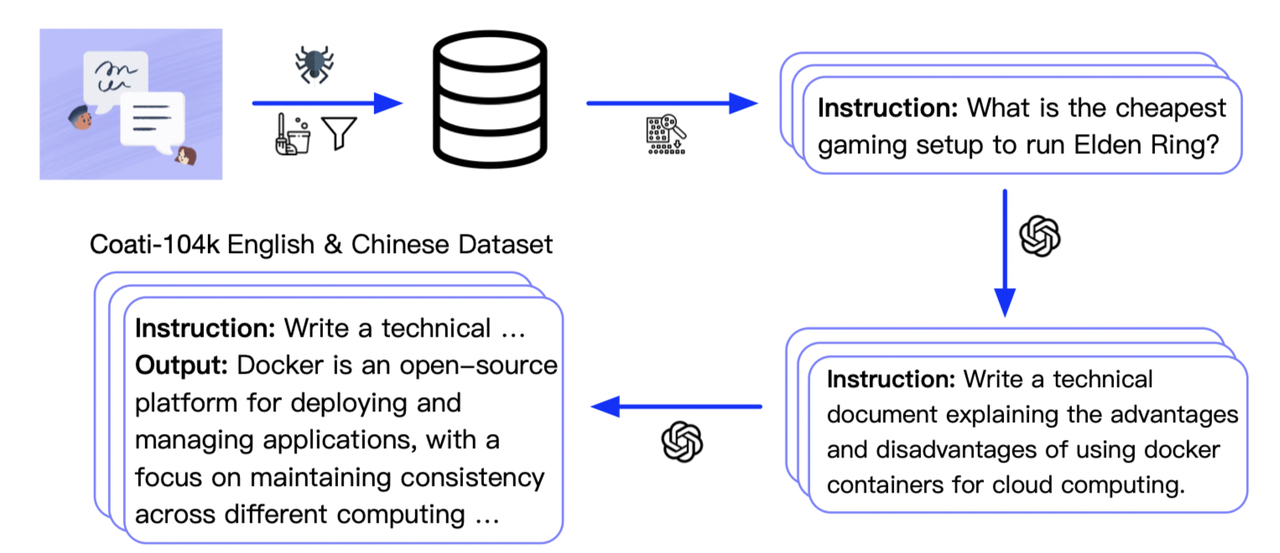
Conversation dataset generation
In order to further improve the model's ability to handle multi-turn conversations, we need to include samples with multi-turn conversations in the dataset. However, the samples in InstructWild and Alpaca datasets currently consist of only single-turn conversations, and their dataset organization is not suitable for storing multi-turn conversations. Additionally, after converting the aforementioned datasets, we also need to include multi-turn conversation datasets like ShareGPT, and we should transform them into the training format supported by ColossalChat.
A sample of conversation dataset should have the following fields:
type(str, optional): The type of the data sample.language(str, optional): The language of the data sample.dataset(str, optional): The dataset the data sample originates from.conversations(str, compulsory): Conversation content of the data sample.id(int, optional): The ID of the data sample.
A simple example:
{
"type": "instruction",
"language": "English",
"dataset": "Alpaca",
"conversations": [
{
"from": "human",
"value": "Give three tips for staying healthy."
},
{
"from": "gpt",
"value": "1.Eat a balanced diet and make sure to include plenty of fruits and vegetables. \n2. Exercise regularly to keep your body active and strong. \n3. Get enough sleep and maintain a consistent sleep schedule."
}
],
"id": 1
}
NOTE: Only key
conversationsis compulsary for training and other keys serve as metadata. The length ofconversationsvaries.
You can run the examples/generate_conversation_dataset.py to generate a conversation dataset supported by ColossalChat.
You can use the following cmd to generate conversation dataset.
python generate_conversation_dataset.py \
--dataset "All"
--save_path "/path/to/dataset"
Stage1 - Supervised instructs tuning
Stage1 is supervised instructs fine-tuning, which uses the datasets mentioned earlier to fine-tune the model. [Stage1 tutorial video]
You can run the examples/train_sft.sh to start a supervised instructs fine-tuning.
You can also use the following cmd to start a supervised instructs fine-tuning with your own settings.
torchrun --standalone --nproc_per_node=4 train_sft.py \
--pretrain "/path/to/LLaMa-7B/" \
--model 'llama' \
--strategy colossalai_zero2 \
--log_interval 10 \
--save_path /path/to/Coati-7B \
--dataset /path/to/data.json \
--batch_size 4 \
--accumulation_steps 8 \
--lr 2e-5 \
--max_datasets_size 512 \
--max_epochs 1 \
--grad_checkpoint
Arg List
- --strategy: the strategy using for training, choices=['ddp', 'colossalai_gemini', 'colossalai_zero2'], default='colossalai_zero2'
- --model: model type, choices=['gpt2', 'bloom', 'opt', 'llama'], default='bloom'
- --pretrain: pretrain model, type=str, default=None
- --max_datasets_size: the max size of dataset, type=int, default=None
- --save_path: path to save the model, type=str, default='output'
- --need_optim_ckpt: whether to save optim ckpt, type=bool, default=False
- --max_epochs: max epochs for training, type=int, default=3
- --batch_size: batch size while training, type=int, default=4
- --lora_rank: low-rank adaptation matrices rank, type=int, default=0
- --log_interval: how many steps to log, type=int, default=100
- --grad_checkpoint: enable gradient checkpointing, type=bool, default=False
Stage2 - Training reward model
We train a reward model in stage 2, which obtains corresponding scores by manually ranking different outputs for the same prompt and supervises the training of the reward model. [Stage2 tutorial video]
You can run the examples/train_rm.sh to start a reward model training.
You can also use the following cmd to start training a reward model.
torchrun --standalone --nproc_per_node=4 train_reward_model.py \
--pretrain "/path/to/LLaMa-7B/" \
--model 'llama' \
--strategy colossalai_zero2 \
--loss_fn 'log_exp'\
--save_path 'rmstatic.pt' \
Features and tricks in RM training
- We support Anthropic/hh-rlhfandrm-static datasets.
- We support 2 kinds of loss_function named 'log_sig'(used by OpenAI) and 'log_exp'(used by Anthropic).
- We change the loss to valid_acc and pair_dist to monitor progress during training.
- We add special token to the end of the sequence to get better result.
- We use cosine-reducing lr-scheduler for RM training.
- We set value_head as 1 liner layer and initialize the weight of value_head using N(0,1/(d_model + 1)) distribution.
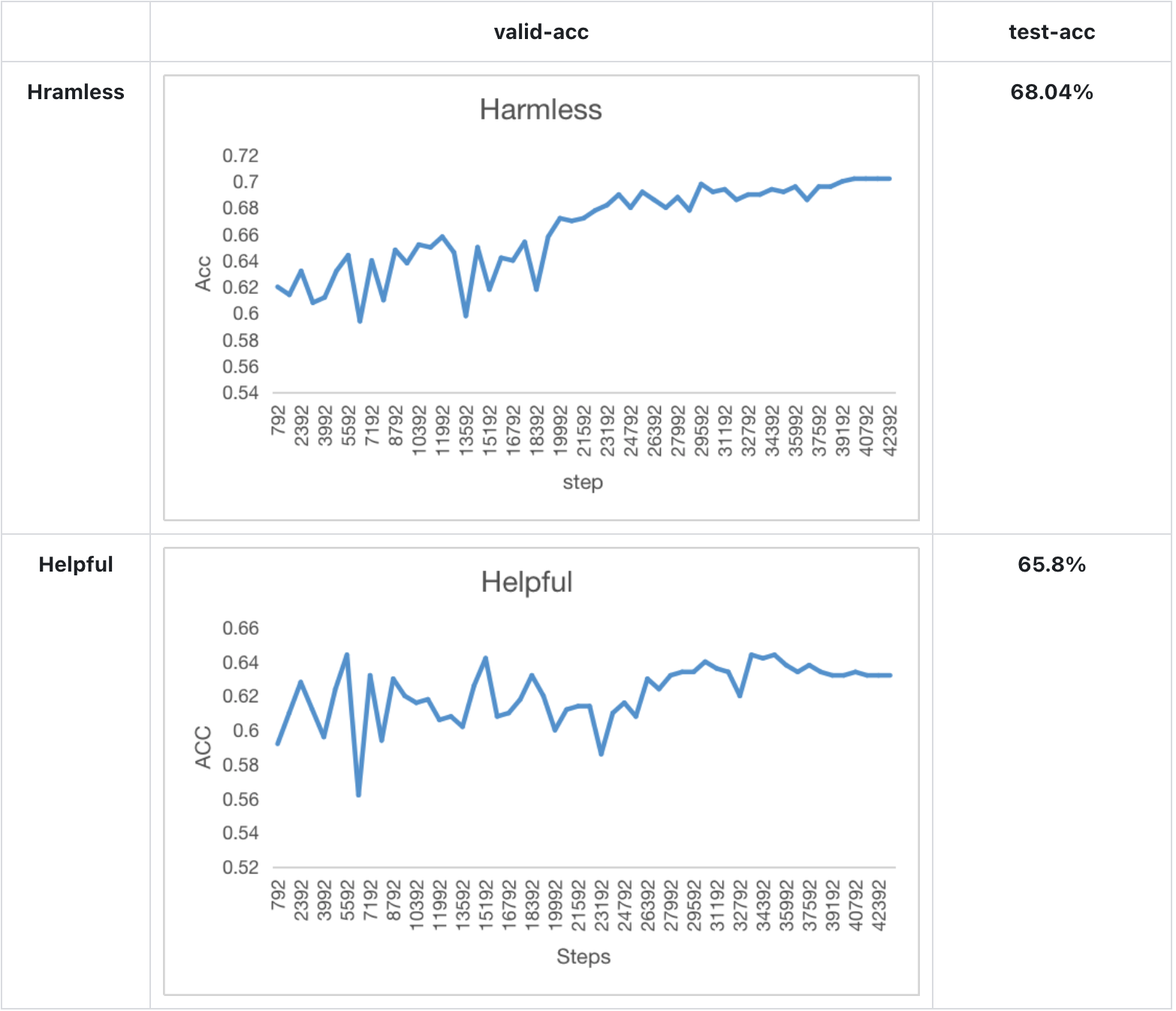
- We train a Bloom-560m reward model for 1 epoch and find the test acc of the model achieve the performance mentions in Anthropics paper.
Experiment result
Model performance in Anthropics paper:

Arg List
- --strategy: the strategy using for training, choices=['ddp', 'colossalai_gemini', 'colossalai_zero2'], default='colossalai_zero2'
- --model: model type, choices=['gpt2', 'bloom', 'opt', 'llama'], default='bloom'
- --pretrain: pretrain model, type=str, default=None
- --model_path: the path of rm model(if continue to train), type=str, default=None
- --save_path: path to save the model, type=str, default='output'
- --need_optim_ckpt: whether to save optim ckpt, type=bool, default=False
- --max_epochs: max epochs for training, type=int, default=3
- --dataset: dataset name, type=str, choices=['Anthropic/hh-rlhf', 'Dahoas/rm-static']
- --subset: subset of the dataset, type=str, default=None
- --batch_size: batch size while training, type=int, default=4
- --lora_rank: low-rank adaptation matrices rank, type=int, default=0
- --loss_func: which kind of loss function, choices=['log_sig', 'log_exp']
- --max_len: max sentence length for generation, type=int, default=512
- --test: whether is only testing, if it's true, the dataset will be small
Stage3 - Training model using prompts with RL
Stage3 uses reinforcement learning algorithm, which is the most complex part of the training process, as shown below:
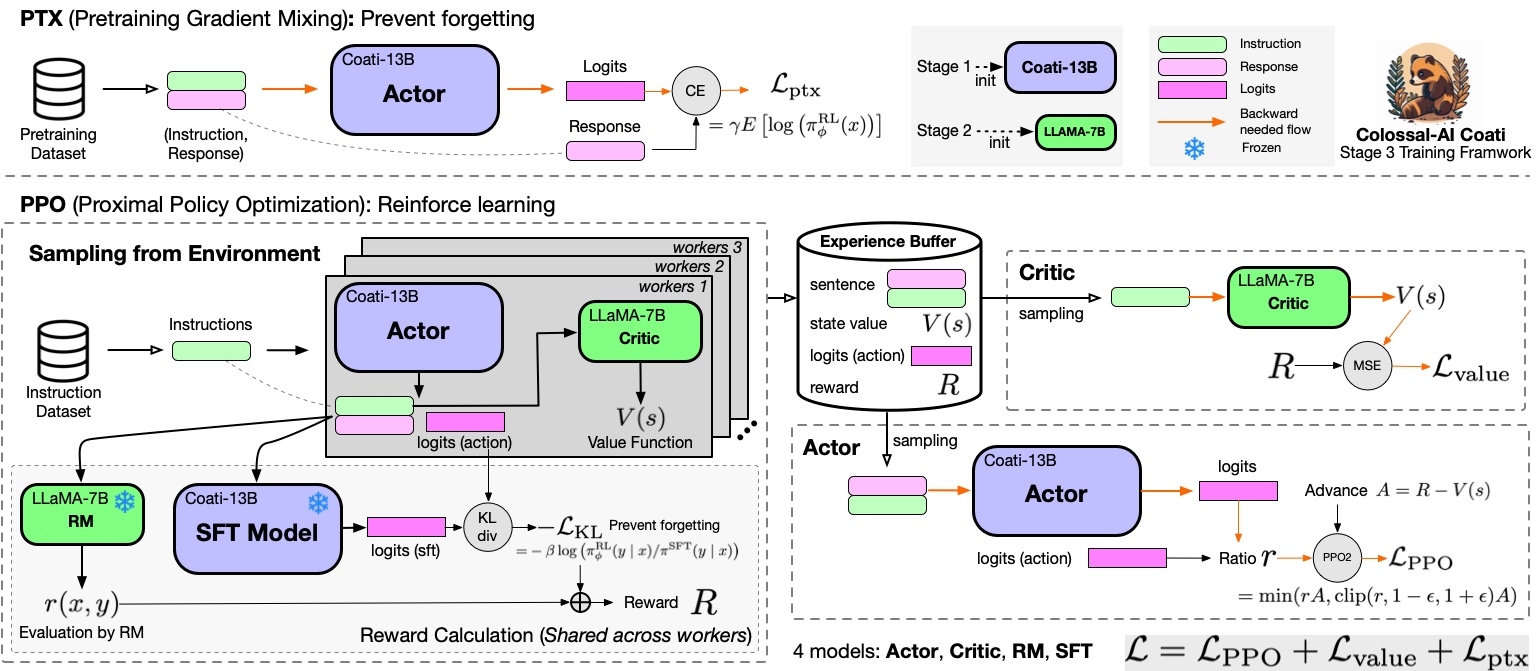
You can run the examples/train_prompts.sh to start PPO training.
You can also use the cmd following to start PPO training.
[Stage3 tutorial video]
torchrun --standalone --nproc_per_node=4 train_prompts.py \
--pretrain "/path/to/LLaMa-7B/" \
--model 'llama' \
--strategy colossalai_zero2 \
--prompt_dataset /path/to/your/prompt_dataset \
--pretrain_dataset /path/to/your/pretrain_dataset \
--rm_pretrain /your/pretrain/rm/definition \
--rm_path /your/rm/model/path
Prompt dataset: the instruction dataset mentioned in the above figure which includes the instructions, e.g. you can use the script which samples instinwild_en.json or instinwild_ch.json in InstructionWild to generate the prompt dataset.
Pretrain dataset: the pretrain dataset including the instruction and corresponding response, e.g. you can use the InstructWild Data in stage 1 supervised instructs tuning.
Arg List
- --strategy: the strategy using for training, choices=['ddp', 'colossalai_gemini', 'colossalai_zero2'], default='colossalai_zero2'
- --model: model type of actor, choices=['gpt2', 'bloom', 'opt', 'llama'], default='bloom'
- --pretrain: pretrain model, type=str, default=None
- --rm_model: reward model type, type=str, choices=['gpt2', 'bloom', 'opt', 'llama'], default=None
- --rm_pretrain: pretrain model for reward model, type=str, default=None
- --rm_path: the path of rm model, type=str, default=None
- --save_path: path to save the model, type=str, default='output'
- --prompt_dataset: path of the prompt dataset, type=str, default=None
- --pretrain_dataset: path of the ptx dataset, type=str, default=None
- --need_optim_ckpt: whether to save optim ckpt, type=bool, default=False
- --num_episodes: num of episodes for training, type=int, default=10
- --num_update_steps: number of steps to update policy per episode, type=int
- --num_collect_steps: number of steps to collect experience per episode, type=int
- --train_batch_size: batch size while training, type=int, default=8
- --ptx_batch_size: batch size to compute ptx loss, type=int, default=1
- --experience_batch_size: batch size to make experience, type=int, default=8
- --lora_rank: low-rank adaptation matrices rank, type=int, default=0
- --kl_coef: kl_coef using for computing reward, type=float, default=0.1
- --ptx_coef: ptx_coef using for computing policy loss, type=float, default=0.9
Inference example - After Stage3
We support different inference options, including int8 and int4 quantization.
For details, see inference/.
Attention
The examples are demos for the whole training process.You need to change the hyper-parameters to reach great performance.
data
- rm-static
- hh-rlhf
- openai/summarize_from_feedback
- openai/webgpt_comparisons
- Dahoas/instruct-synthetic-prompt-responses
Support Model
GPT
- GPT2-S (s)
- GPT2-M (m)
- GPT2-L (l)
- GPT2-XL (xl)
- GPT2-4B (4b)
- GPT2-6B (6b)
BLOOM
OPT
LLaMA
- LLaMA-7B
- LLaMA-13B
- LLaMA-33B
- LLaMA-65B
Add your own models
If you want to support your own model in Coati, please refer the pull request for RoBERTa support as an example --[chatgpt] add pre-trained model RoBERTa for RLHF stage 2 & 3, and submit a PR to us.
You should complete the implementation of four model classes, including Reward model, Critic model, LM model, Actor model
here are some example code for a NewModel named Coati.
if it is supported in huggingface transformers, you can load it by from_pretrained, o
r you can build your own model by yourself.
Actor model
from ..base import Actor
from transformers.models.coati import CoatiModel
class CoatiActor(Actor):
def __init__(self,
pretrained: Optional[str] = None,
checkpoint: bool = False,
lora_rank: int = 0,
lora_train_bias: str = 'none') -> None:
if pretrained is not None:
model = CoatiModel.from_pretrained(pretrained)
else:
model = build_model() # load your own model if it is not support in transformers
super().__init__(model, lora_rank, lora_train_bias)
Reward model
from ..base import RewardModel
from transformers.models.coati import CoatiModel
class CoatiRM(RewardModel):
def __init__(self,
pretrained: Optional[str] = None,
checkpoint: bool = False,
lora_rank: int = 0,
lora_train_bias: str = 'none') -> None:
if pretrained is not None:
model = CoatiModel.from_pretrained(pretrained)
else:
model = build_model() # load your own model if it is not support in transformers
value_head = nn.Linear(model.config.n_embd, 1)
value_head.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=1 / (model.config.n_embd + 1))
super().__init__(model, value_head, lora_rank, lora_train_bias)
Critic model
from ..base import Critic
from transformers.models.coati import CoatiModel
class CoatiCritic(Critic):
def __init__(self,
pretrained: Optional[str] = None,
checkpoint: bool = False,
lora_rank: int = 0,
lora_train_bias: str = 'none') -> None:
if pretrained is not None:
model = CoatiModel.from_pretrained(pretrained)
else:
model = build_model() # load your own model if it is not support in transformers
value_head = nn.Linear(model.config.n_embd, 1)
value_head.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=1 / (model.config.n_embd + 1))
super().__init__(model, value_head, lora_rank, lora_train_bias)