10 KiB
⚡️ ShardFormer
📚 Table of Contents
🔗 Introduction
Shardformer is a module that automatically parallelizes the mainstream models in libraries such as HuggingFace and TIMM. This module aims to make parallelization hassle-free for users who are not from the system background.
🔨 Usage
Quick Start
The sample API usage is given below:
from colossalai.shardformer import ShardConfig, Shard
from transformers import BertForMaskedLM
# launch colossalai
colossalai.launch_from_torch()
# create model
config = BertConfig.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
model = BertForMaskedLM.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased', config=config)
# create huggingface model as normal
shard_config = ShardConfig(tensor_parallel_size=2,
data_parallel_size=1,
gather_output=True)
shard_former = ShardFormer(shard_config=shard_config)
shard_former.init_distributed()
sharded_model = shard_former.shard_model(model).to('cuda')
# do everything like normal
...
Write your own policy
If you have a custom model, you can also use Shardformer to parallelize it by writing your own sharding policy. More information about the sharding policy can be found in API Design.
from colossalai.shardformer import Policy
class MyPolicy(Policy):
# implement your own policy
...
# init model and shard former
...
# use customized policy to shard model
my_policy = MyPolicy()
shard_former.shard_model(model, my_policy)
🗺 Roadmap
We will follow this roadmap to develop Shardformer:
- API Design
- API Implementation
- Unit Testing
- Policy Implementation
- Hugging Face
- NLP
- BERT
- T5
- LlaMa
- GPT2
- OPT
- BLOOM
- GLM
- RoBERTa
- ALBERT
- ERNIE
- GPT Neo
- GPT-J
- CV
- ViT
- BEiT
- SwinTransformer
- SwinTransformer V2
- Audio
- Whisper
- Multi-modal
- To be added
- NLP
- Hugging Face
💡 API Design
We will discuss the major components of ShardFormer below to help you better understand how things work.
This section serves as the design doc for Shardformer and the function signature might differ from the actual implementation.
Please refer to the code for more details.
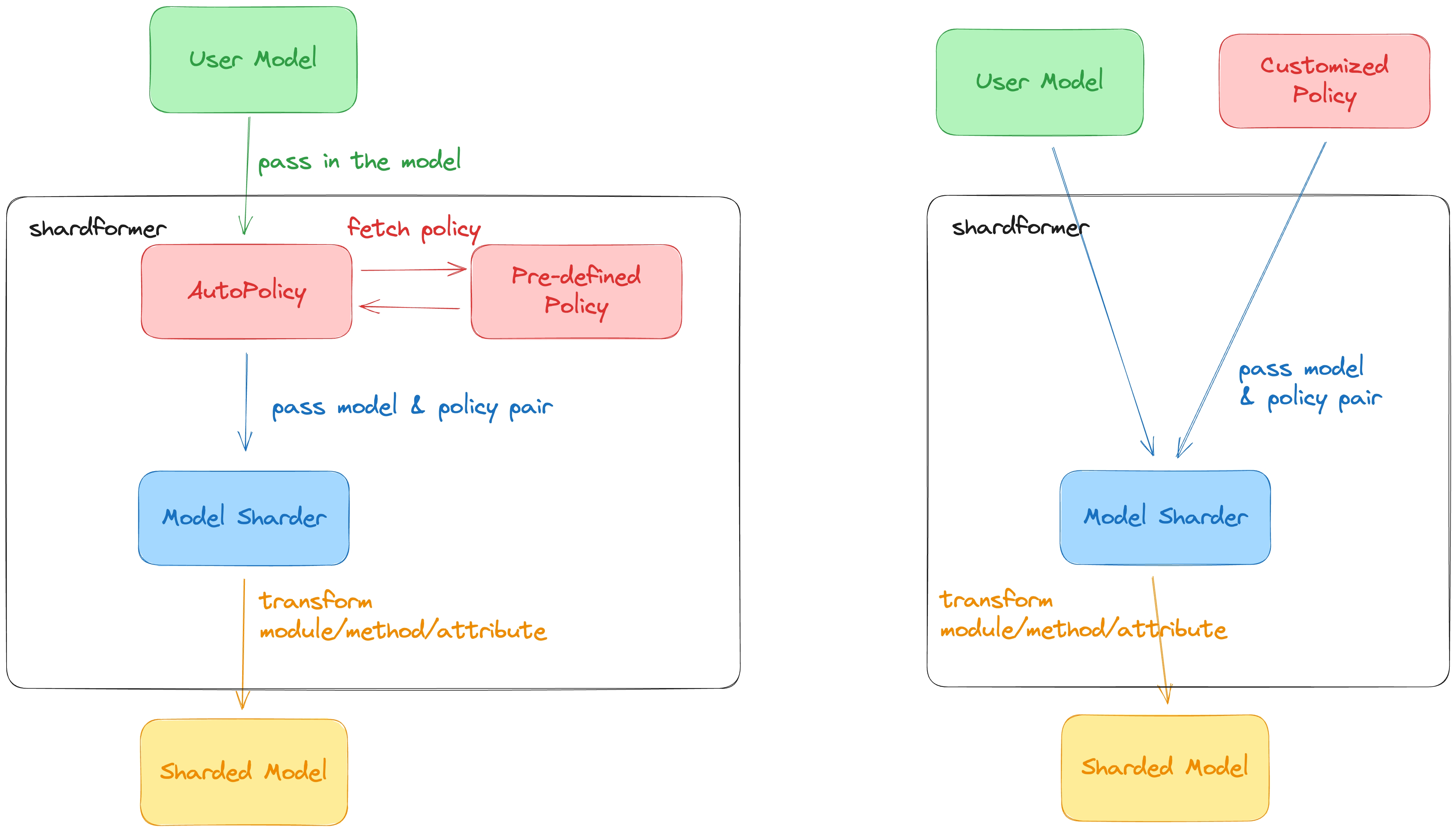
This diagram is deprecated, need to update it
Distributed Modules
ShardFormer replaces the original PyTorch module with a distributed module.
The distributed module keeps the same attributes as the original module but replaces the original parameters with distributed parameters and defines a new forward function to execute distributed computation.
Each distributed module implements its from_native_module static method to convert the PyTorch module to its corresponding distributed module.
class ParallelModule(torch.nn.Module):
@abstractmethod
def from_native_module(module: torch.nn.Module, process_group: Union[ProcessGroup, Tuple[ProcessGroup]]) -> ParallelModule
"""
Convert a native module to a parallelized
Examples:
```python
# replace module
my_linear = Linear1D_Col.from_native_module(my_linear, process_group)
```
"""
Shard Config
ShardConfig is a simple data class to tell ShardFormer how sharding will be performed.
@dataclass
class ShardConfig:
data_parallel_size: int
tensor_parallel_size: int
...
# Some possible future config fields
pipeline_parallel_size: int # Support pipeline parallelism
tensor_parallel_mode: Choice['1d', '2d', '2.5d', '3d'] # support different tensor parallel mode
inference_only: bool # only inject inference-suitable sharding policy
gather_output: bool # gather the model output
use_flash_attention: bool # whether to use flash attention to speed up attention
Policy
The Policy class describes how to handle the model sharding.
It is merely a description, the actual sharding will be performed by ModelSharder.
We abstract the policy into four stages:
- Preprocessing: call
Policy.preprocessto do some prior work before sharding, for example, resizing the embedding - Providing a new class: call
Policy.new_model_classto get a new class for the model, this class replaces attributes and the forward function - Providing
ModulePolicyDescription: callPolicy.module_policyto get a bunch ofModulePolicyDescriptionto tellModelSharderhow the submodules's attributes, child parameters, and deeper submodules will be substituted. - Postprocessing: call
Policy.postprocessto perform some postprocessing work, for example, binding the embedding and classifier head weights of the BERT model.
@dataclass
class ModulePolicyDescription:
"""
Describe how the attributes and parameters will be transformed in a policy
Args:
attribute_replacement (Dict[str, Any]): key is the attribute name, value is the attribute value after sharding
param_replacement (List[Callable]): a list of functions to perform in-place param replacement. The function must receive two arguments: module, process_group. One example is
def example_replace_weight(module: torch.nn.Module, process_group):
weight = module.weight
new_weight = shard_rowwise(weight, process_group)
module.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(new_weight)
sub_module_replacement: each element in the list is a ParamReplacementDescription object which specifies the module to be replaced and the target module used to replacement
"""
attribute_replacement: Dict[str, Any]
param_replacement: List[Callable]
sub_module_replacement: List[SubModuleReplacementDescription]
@dataclass
class SubModuleReplacementDescription:
"""
Describe how a submodule will be replaced
Args:
suffix (str): used to get the submodule object
target_module (ParallelModule): specifies the module class used to replace to submodule
kwargs (Dict[str, Any]): the dictionary used to pass extra arguments to the `ParallelModule.from_native_module` method.
"""
suffix: str
target_module: ParallelModule
kwargs: Dict[str, Any] = None
class Policy(ABC):
def __init__(self)
self.model = None
def set_model(self, model: nn.Module) -> None:
"""
Set model as an attribute of the Policy object so that we can access the model's attributes.
"""
self.model = model
@abstractmethod
def preprocess(self) -> nn.Module:
"""
Perform some preprocessing on the model, such as resizing the embedding size
"""
...
@abstractmethod
def module_policy(self) -> Dict[Union[str, nn.Module], ModulePolicyDescription]:
"""
Return the dict for the modify policy, the key is the original layer class and the value is the
argument for the modify layer
"""
...
@abstractmethod
def new_model_class(self) -> Union[Type[nn.Module], None]:
"""
replace the class of the model to substitute the forward and attributes
"""
...
@abstractmethods
def postprocess(self) -> nn.Module:
"""
Perform some postprocessing on the model, such as binding the embedding with the weight of the classifier head
"""
...
Model Sharder
ModelSharder is the class in charge of sharding the model based on the given policy.
class ModelSharder:
def __init__(self, model: torch.nn.Module, shard_config: ShardConfig, Policy: ShardPolicy = None)
#TODO: input is a cls or a obj
def shard(self) -> None:
"""
Shard model with parallelelism with the help of pre-processing, replace_model_class, replace_module, and post-processing.
"""
...
def replace_model_class(self) -> None:
"""
Replace the model's methods and attributes with our own defined class.
E.g. we can replace the forward function of the original BertForMaskedLM object
with the forward function we define in BertForMaskedLM_ class.
"""
...
def replace_module(self) -> None:
"""
Replace the layer according to the policy. Call Policy.module_policy() to get the module. Call _replace_module recursively.
"""
...
User-facing API
We only expose a limited number of APIs to the user to keep their user experience simple and clean.
class ShardFormer:
"""
Parallelize model based on the given config and policy
Example:
shard_former = ShardFormer(shard_config=shard_config)
shard_former.init_distributed()
model = shard_former.shard_model(model, policy=policy)
dataloader = shard_former.shard_dataset(dataset)
"""
def __init__(self, shard_config: ShardConfig):
"""
Do two things:
1. Create a colossalai.cluster.process_group_manager to manage process groups for dp, tp and pp
2. serve as a store for shard config
"""
self.shard_config = shard_config
self.pg_manager = None
def init_distributed(self) -> colossalai.cluster.ProcessGroupManager:
"""
Initialize the distributed process group according to the
"""
pg_manager = ...
self.pg_manager = pg_manager
return pg_manager
def shard_model(self, model: torch.nn.Module,policy: Policy) -> torch.nn.Module:
"""
Shard model for TP and PP
"""
...
def shard_dataset(self, dataset: Dataset) -> Dataloader:
"""
Shard dataset for DP
"""
...