* [test] added spawn decorator * polish code * polish code * polish code * polish code * polish code * polish code |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| benchmarks | ||
| coati | ||
| examples | ||
| inference | ||
| tests | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| pytest.ini | ||
| requirements-test.txt | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| setup.py | ||
| version.txt | ||
README.md

ColossalChat
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- What is ColossalChat and Coati ?
- Online demo
- Install
- How to use?
- Coati7B examples
- FAQ
- The Plan
- Invitation to open-source contribution
- Quick Preview
- Authors
- Citations
- Licenses
What is ColossalChat and Coati ?
ColossalChat is the project to implement LLM with RLHF, powered by the Colossal-AI project.
Coati stands for ColossalAI Talking Intelligence. It is the name for the module implemented in this project and is also the name of the large language model developed by the ColossalChat project.
The Coati package provides a unified large language model framework that has implemented the following functions
- Supports comprehensive large-model training acceleration capabilities for ColossalAI, without requiring knowledge of complex distributed training algorithms
- Supervised datasets collection
- Supervised instructions fine-tuning
- Training reward model
- Reinforcement learning with human feedback
- Quantization inference
- Fast model deploying
- Perfectly integrated with the Hugging Face ecosystem, a high degree of model customization
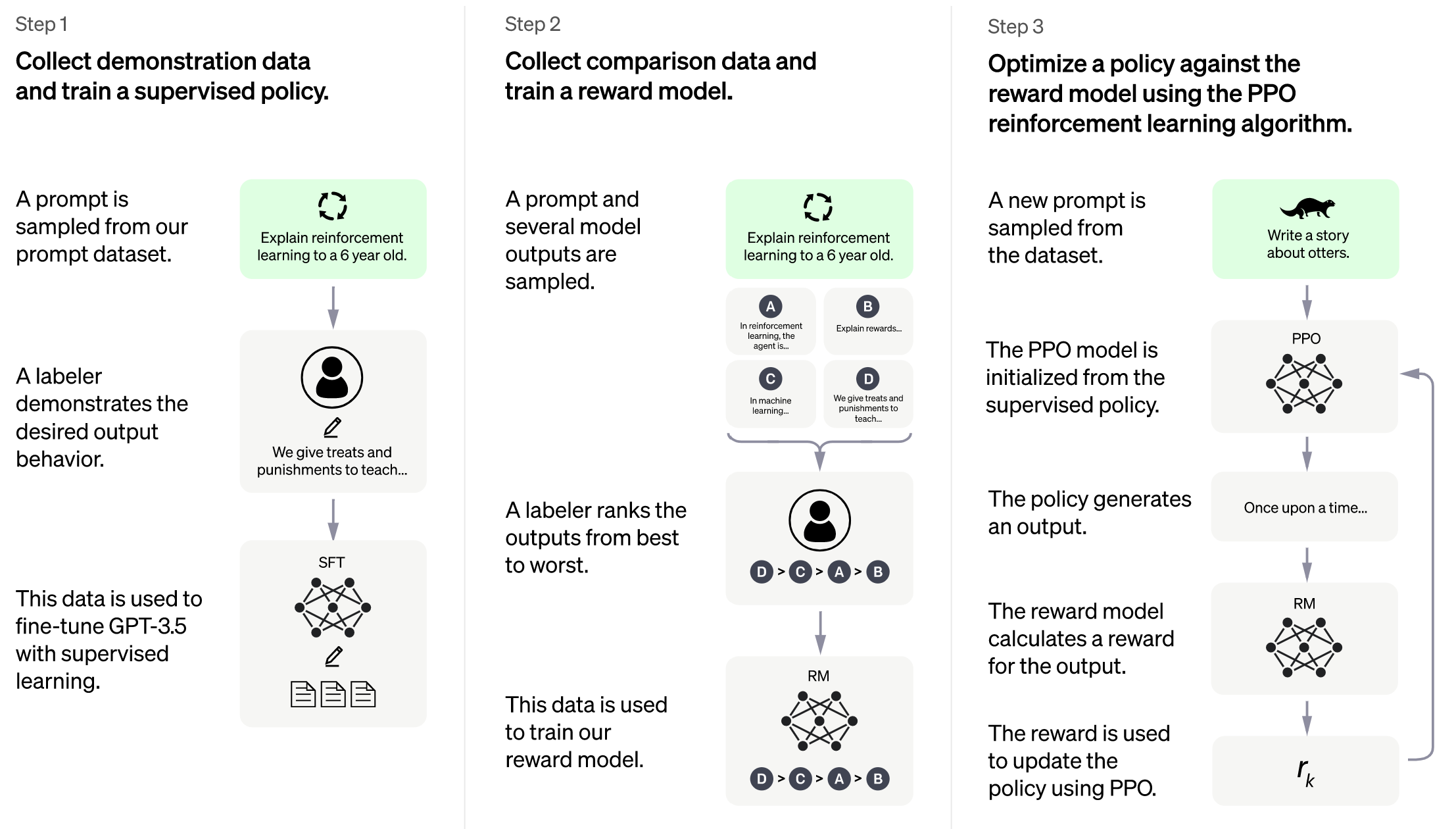
Image source: https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
As Colossa-AI is undergoing some major updates, this project will be actively maintained to stay in line with the Colossal-AI project.
More details can be found in the latest news.
- [2023/03] ColossalChat: An Open-Source Solution for Cloning ChatGPT With a Complete RLHF Pipeline
- [2023/02] Open Source Solution Replicates ChatGPT Training Process! Ready to go with only 1.6GB GPU Memory
Online demo
You can experience the performance of Coati7B on this page.
Due to resource constraints, we will only provide this service from 29th Mar 2023 to 5 April 2023. However, we have provided the inference code in the inference folder. The WebUI will be open-sourced soon as well.
Warning: Due to model and dataset size limitations, Coati is just a baby model, Coati7B may output incorrect information and lack the ability for multi-turn dialogue. There is still significant room for improvement.
Install
Install the environment
conda create -n coati
conda activate coati
pip install .
Install the Transformers
Given Hugging Face hasn't officially supported the LLaMA models, We fork a branch of Transformers that can be compatible with our code
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/transformers
cd transformers
pip install .
How to use?
Supervised datasets collection
we collected 104K bilingual datasets of Chinese and English, and you can find the datasets in this repo InstructionWild
Here is how we collected the data
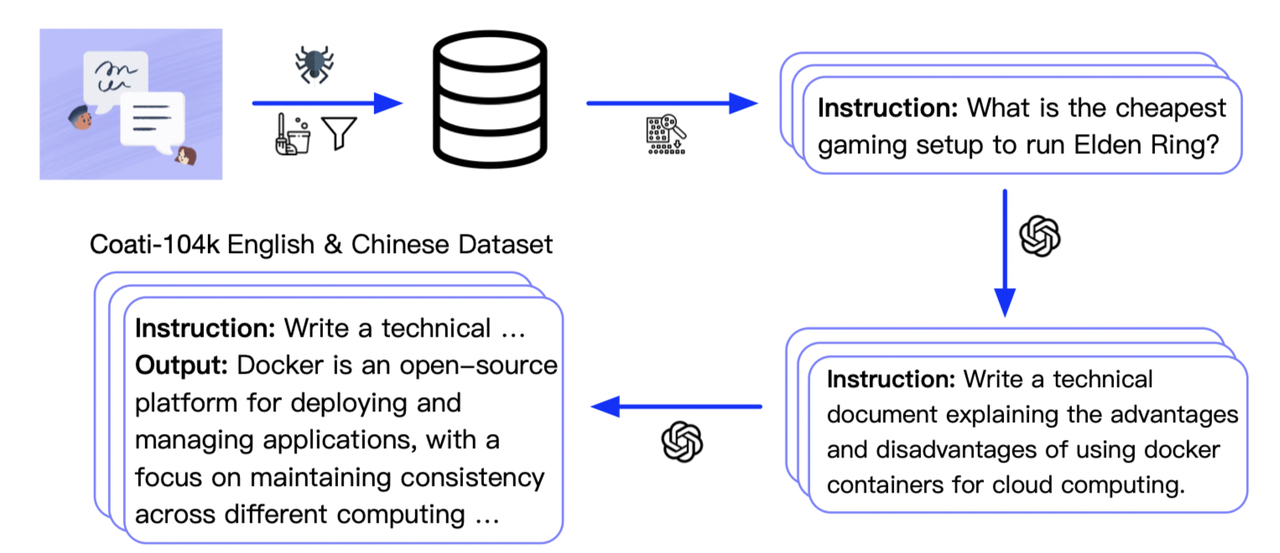
Stage1 - Supervised instructs tuning
Stage1 is supervised instructs fine-tuning, which uses the datasets mentioned earlier to fine-tune the model
you can run the examples/train_sft.sh to start a supervised instructs fine-tuning
torchrun --standalone --nproc_per_node=4 train_sft.py \
--pretrain "/path/to/LLaMa-7B/" \
--model 'llama' \
--strategy colossalai_zero2 \
--log_interval 10 \
--save_path /path/to/Coati-7B \
--dataset /path/to/data.json \
--batch_size 4 \
--accimulation_steps 8 \
--lr 2e-5 \
--max_datasets_size 512 \
--max_epochs 1 \
Stage2 - Training reward model
Stage2 trains a reward model, which obtains corresponding scores by manually ranking different outputs for the same prompt and supervises the training of the reward model
you can run the examples/train_rm.sh to start a reward model training
torchrun --standalone --nproc_per_node=4 train_reward_model.py
--pretrain "/path/to/LLaMa-7B/" \
--model 'llama' \
--strategy colossalai_zero2 \
--loss_fn 'log_exp'\
--save_path 'rmstatic.pt' \
Stage3 - Training model with reinforcement learning by human feedback
Stage3 uses reinforcement learning algorithm, which is the most complex part of the training process:
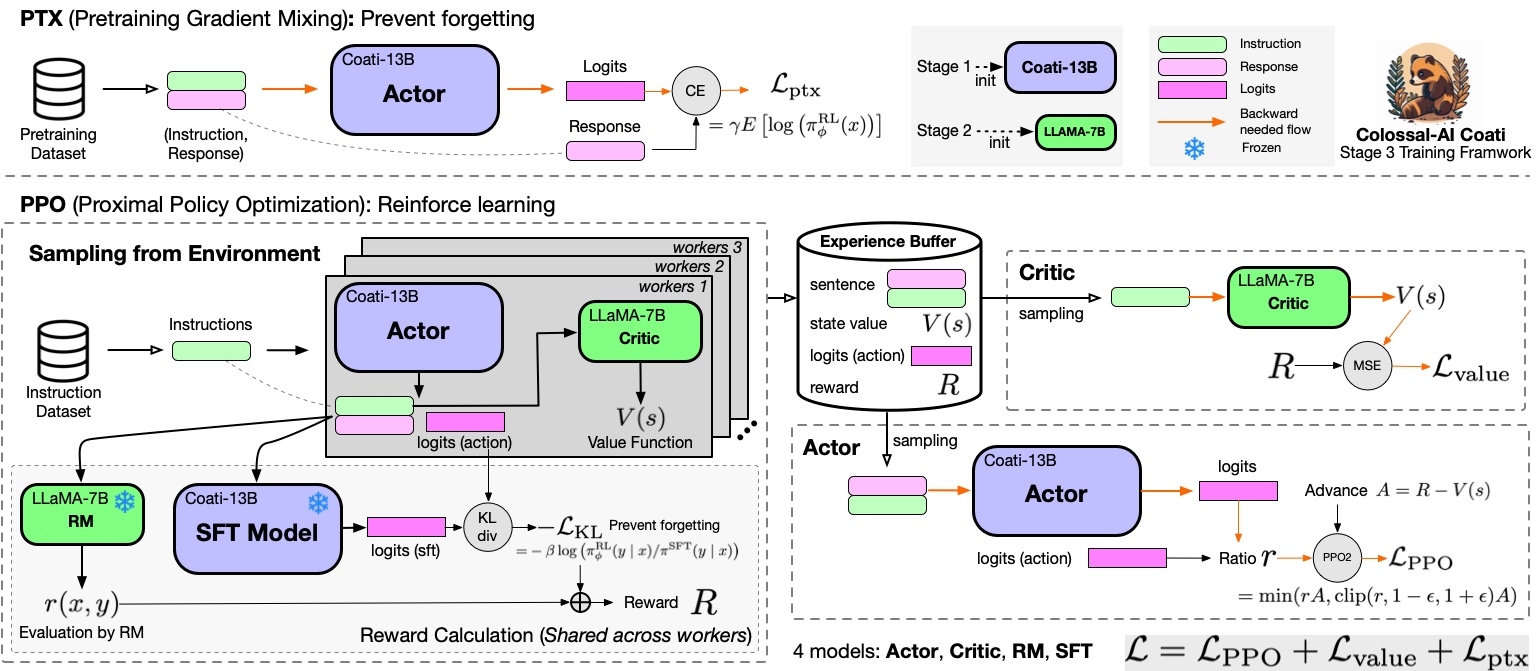
you can run the examples/train_prompts.sh to start training PPO with human feedback
torchrun --standalone --nproc_per_node=4 train_prompts.py \
--pretrain "/path/to/LLaMa-7B/" \
--model 'llama' \
--strategy colossalai_zero2 \
--prompt_path /path/to/your/prompt_dataset \
--pretrain_dataset /path/to/your/pretrain_dataset \
--rm_pretrain /your/pretrain/rm/defination \
--rm_path /your/rm/model/path
For more details, see examples/.
Inference - After Training
8-bit setup
8-bit quantization is originally supported by the latest transformers. Please install it from source.
Please ensure you have downloaded HF-format model weights of LLaMA models.
Usage:
from transformers import LlamaForCausalLM
USE_8BIT = True # use 8-bit quantization; otherwise, use fp16
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"pretrained/path",
load_in_8bit=USE_8BIT,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="auto",
)
if not USE_8BIT:
model.half() # use fp16
model.eval()
Troubleshooting: if you get errors indicating your CUDA-related libraries are not found when loading the 8-bit model, you can check whether your LD_LIBRARY_PATH is correct.
E.g. you can set export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$CUDA_HOME/lib64:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
4-bit setup
Please ensure you have downloaded the HF-format model weights of LLaMA models first.
Then you can follow GPTQ-for-LLaMa. This lib provides efficient CUDA kernels and weight conversion scripts.
After installing this lib, we may convert the original HF-format LLaMA model weights to a 4-bit version.
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python llama.py /path/to/pretrained/llama-7b c4 --wbits 4 --groupsize 128 --save llama7b-4bit.pt
Run this command in your cloned GPTQ-for-LLaMa directory, then you will get a 4-bit weight file llama7b-4bit-128g.pt.
Troubleshooting: if you get errors about position_ids, you can checkout to commit 50287c3b9ae4a3b66f6b5127c643ec39b769b155(GPTQ-for-LLaMa repo).
For more details, see inference/.
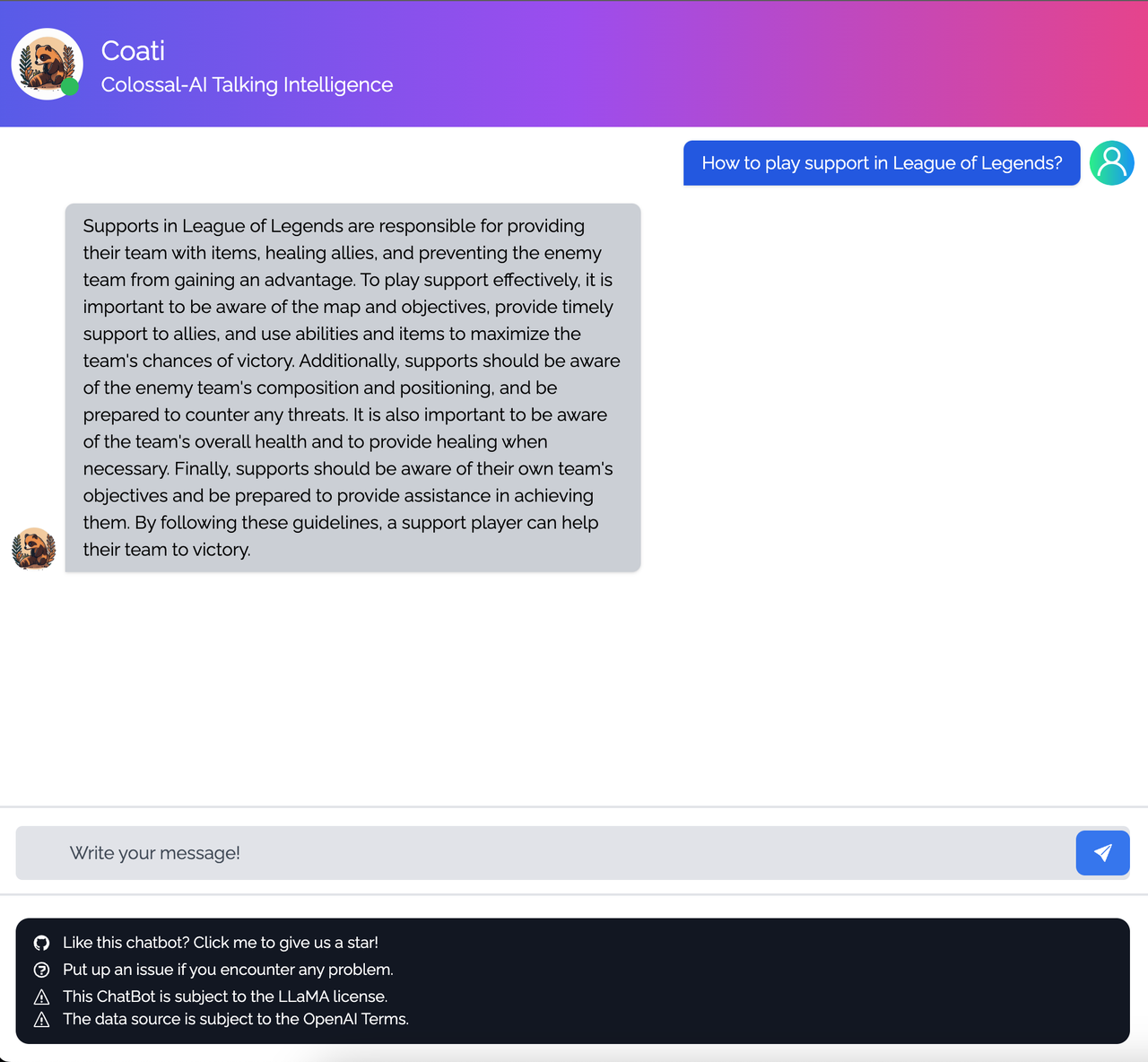
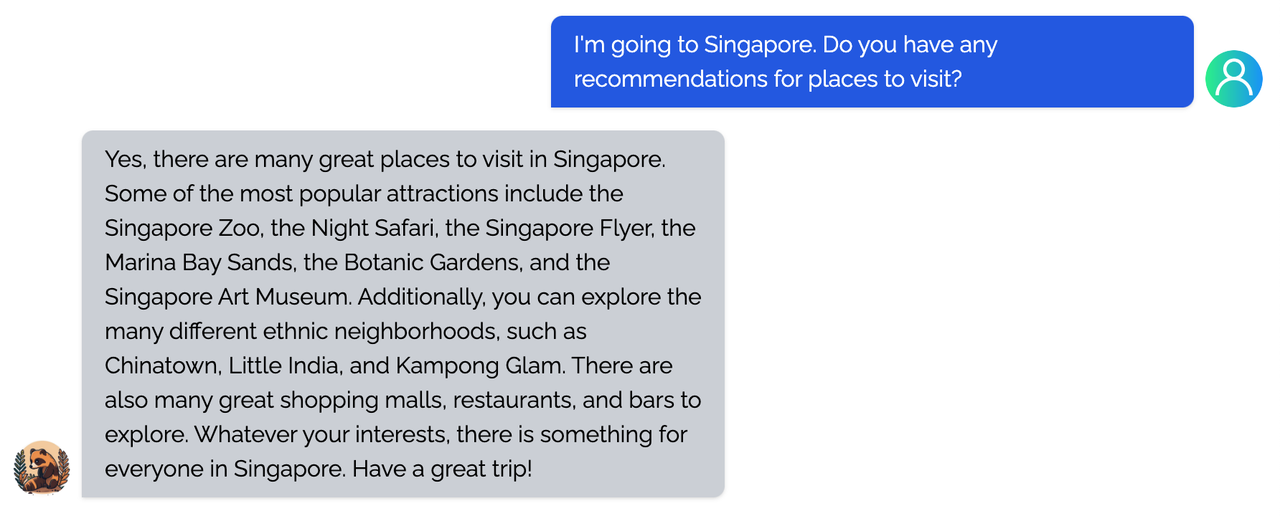
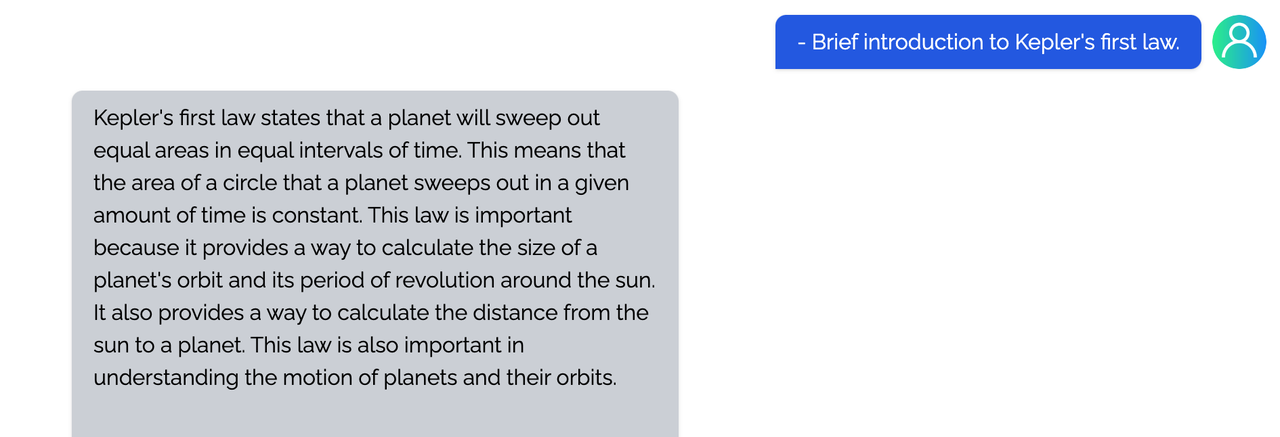
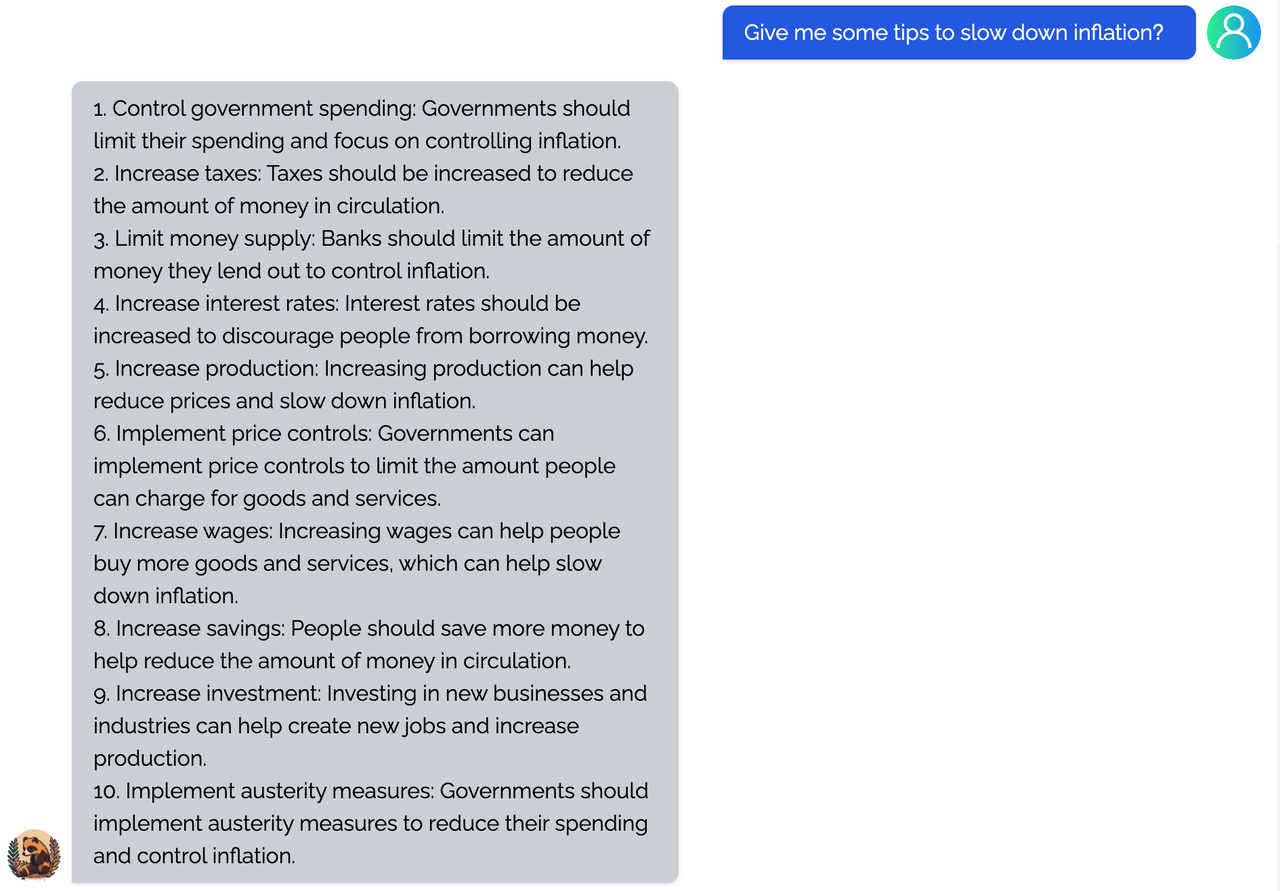
Coati7B examples
Generation
Open QA
You can find more examples in this repo.
Limitation for LLaMA-finetuned models
- Both Alpaca and ColossalChat are based on LLaMA. It is hard to compensate for the missing knowledge in the pre-training stage.
- Lack of counting ability: Cannot count the number of items in a list.
- Lack of Logics (reasoning and calculation)
- Tend to repeat the last sentence (fail to produce the end token).
- Poor multilingual results: LLaMA is mainly trained on English datasets (Generation performs better than QA).
Limitation of dataset
- Lack of summarization ability: No such instructions in finetune datasets.
- Lack of multi-turn chat: No such instructions in finetune datasets
- Lack of self-recognition: No such instructions in finetune datasets
- Lack of Safety:
- When the input contains fake facts, the model makes up false facts and explanations.
- Cannot abide by OpenAI's policy: When generating prompts from OpenAI API, it always abides by its policy. So no violation case is in the datasets.
FAQ
How to save/load checkpoint
We have integrated the Transformers save and load pipeline, allowing users to freely call Hugging Face's language models and save them in the HF format.
from coati.models.llama import LlamaLM
from coati.trainer import SFTTrainer
model = LlamaLM(pretrained=args.pretrain)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(args.pretrain)
trainer = SFTTrainer(model=model,
strategy=strategy,
optim=optim,
train_dataloader=train_dataloader,
eval_dataloader=eval_dataloader,
batch_size=args.batch_size,
max_epochs=args.max_epochs,
accimulation_steps = args.accimulation_steps
)
trainer.fit()
trainer.save_model(path=args.save_path, only_rank0=True, tokenizer=tokenizer)
The Plan
- implement PPO fine-tuning
- implement training reward model
- support LoRA
- support inference
- support llama from facebook
- implement PPO-ptx fine-tuning
- integrate with Ray
- support more RL paradigms, like Implicit Language Q-Learning (ILQL),
- support chain-of-thought by langchain
Real-time progress
You will find our progress in github project broad
Invitation to open-source contribution
Referring to the successful attempts of BLOOM and Stable Diffusion, any and all developers and partners with computing powers, datasets, models are welcome to join and build the Colossal-AI community, making efforts towards the era of big AI models from the starting point of replicating ChatGPT!
You may contact us or participate in the following ways:
- Leaving a Star ⭐ to show your like and support. Thanks!
- Posting an issue, or submitting a PR on GitHub follow the guideline in Contributing.
- Join the Colossal-AI community on Slack, and WeChat(微信) to share your ideas.
- Send your official proposal to email contact@hpcaitech.com
Thanks so much to all of our amazing contributors!
Quick Preview
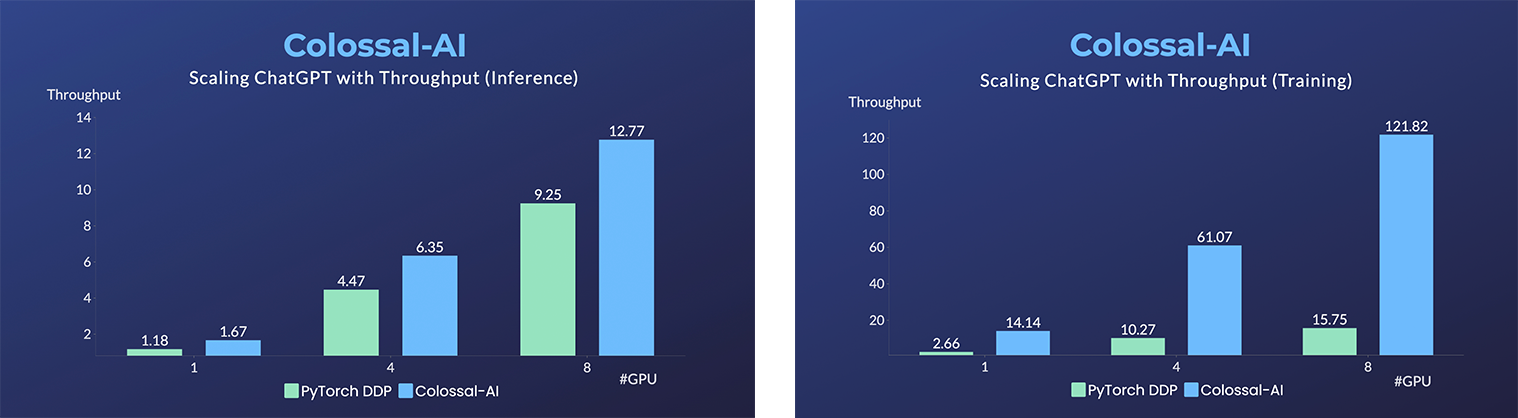
- Up to 7.73 times faster for single server training and 1.42 times faster for single-GPU inference
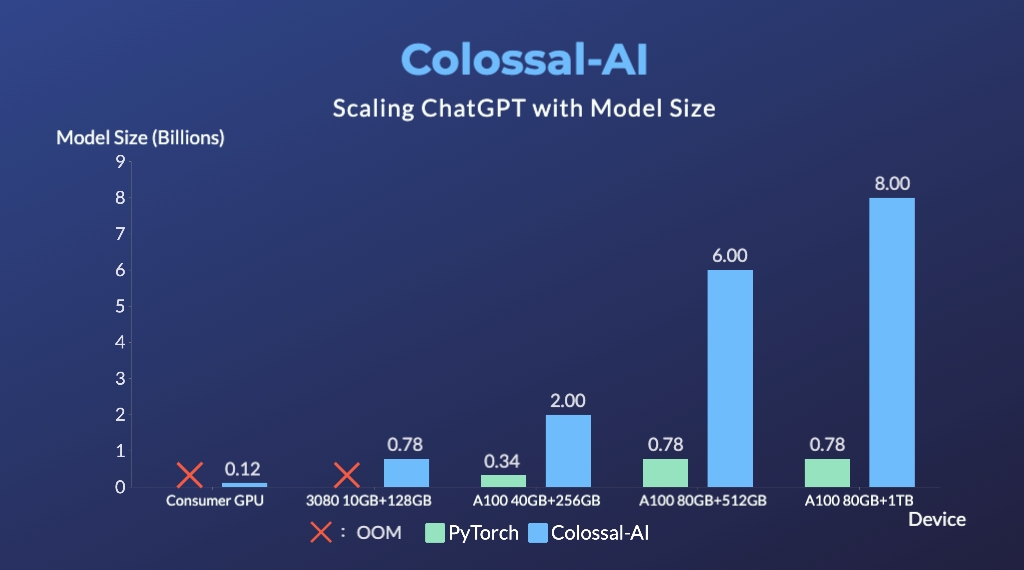
- Up to 10.3x growth in model capacity on one GPU
- A mini demo training process requires only 1.62GB of GPU memory (any consumer-grade GPU)
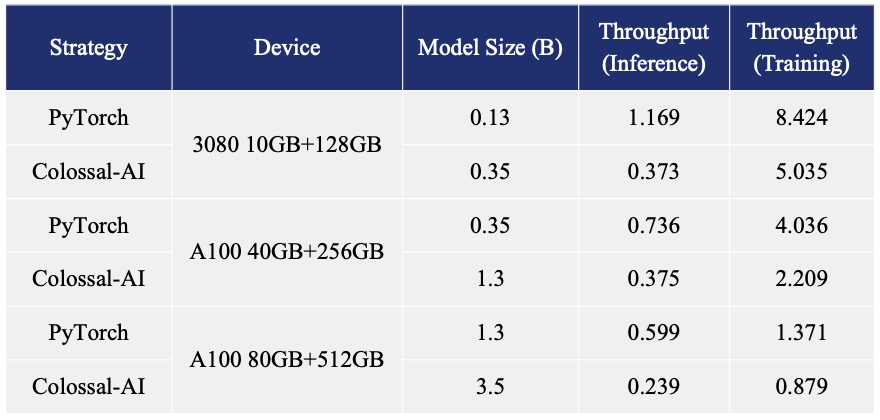
- Increase the capacity of the fine-tuning model by up to 3.7 times on a single GPU
- Keep in a sufficiently high running speed
Authors
Coati is developed by ColossalAI Team:
The Phd student from (HPC-AI) Lab also contributed a lot to this project.
Citations
@article{Hu2021LoRALA,
title = {LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models},
author = {Edward J. Hu and Yelong Shen and Phillip Wallis and Zeyuan Allen-Zhu and Yuanzhi Li and Shean Wang and Weizhu Chen},
journal = {ArXiv},
year = {2021},
volume = {abs/2106.09685}
}
@article{ouyang2022training,
title={Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback},
author={Ouyang, Long and Wu, Jeff and Jiang, Xu and Almeida, Diogo and Wainwright, Carroll L and Mishkin, Pamela and Zhang, Chong and Agarwal, Sandhini and Slama, Katarina and Ray, Alex and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.02155},
year={2022}
}
@article{touvron2023llama,
title={LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models},
author={Touvron, Hugo and Lavril, Thibaut and Izacard, Gautier and Martinet, Xavier and Lachaux, Marie-Anne and Lacroix, Timoth{\'e}e and Rozi{\`e}re, Baptiste and Goyal, Naman and Hambro, Eric and Azhar, Faisal and Rodriguez, Aurelien and Joulin, Armand and Grave, Edouard and Lample, Guillaume},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971},
year={2023}
}
@misc{alpaca,
author = {Rohan Taori and Ishaan Gulrajani and Tianyi Zhang and Yann Dubois and Xuechen Li and Carlos Guestrin and Percy Liang and Tatsunori B. Hashimoto },
title = {Stanford Alpaca: An Instruction-following LLaMA model},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/tatsu-lab/stanford_alpaca}},
}
@misc{instructionwild,
author = {Fuzhao Xue and Zangwei Zheng and Yang You },
title = {Instruction in the Wild: A User-based Instruction Dataset},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/XueFuzhao/InstructionWild}},
}
Licenses
Coati is licensed under the Apache 2.0 License.