|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| app | ||
| assets | ||
| examples/nginx-basic-auth | ||
| test/unit | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .godir | ||
| Dockerfile | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Procfile | ||
| README.md | ||
| bower.json | ||
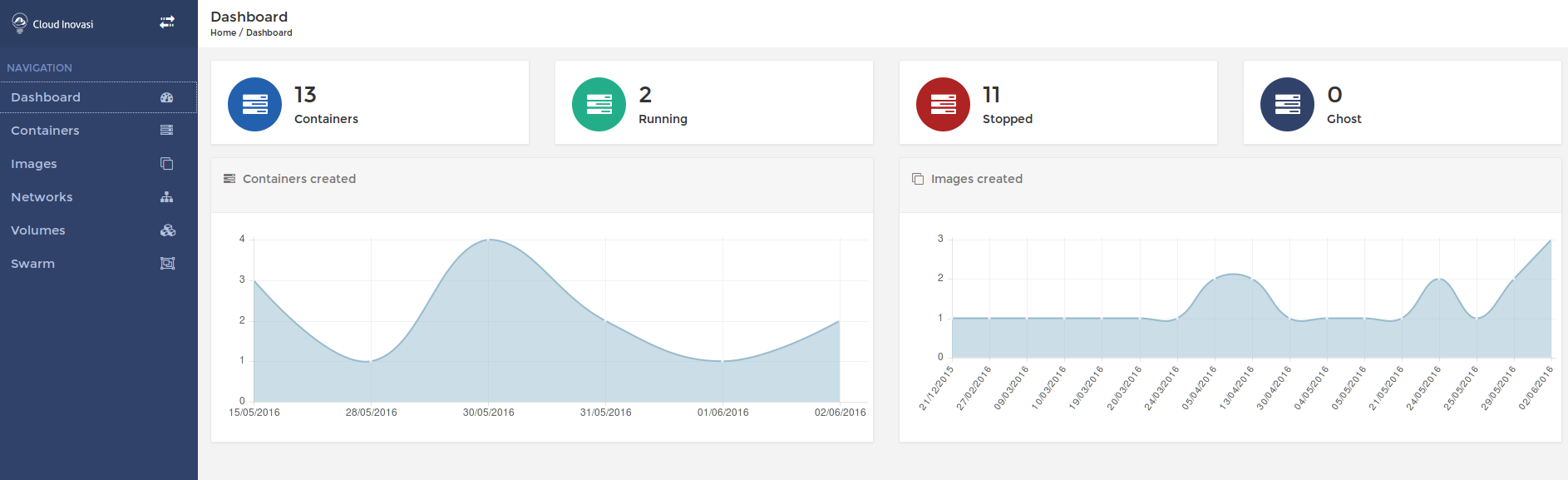
| dashboard.png | ||
| dockerui.go | ||
| gruntFile.js | ||
| index.html | ||
| package.json | ||
README.md
Cloudinovasi UI for Docker
This UI is dedicated to CloudInovasi internal usage.
A fork of the amazing UI for Docker by Michael Crosby and Kevan Ahlquist (https://github.com/kevana/ui-for-docker) using the rdash-angular theme (https://github.com/rdash/rdash-angular).
UI For Docker is a web interface for the Docker Remote API. The goal is to provide a pure client side implementation so it is effortless to connect and manage docker.
Goals
- Minimal dependencies - I really want to keep this project a pure html/js app.
- Consistency - The web UI should be consistent with the commands found on the docker CLI.
Supported Docker versions
The current Docker version support policy is the following: N to N-2 included where N is the latest version.
At the moment, the following versions are supported: 1.9, 1.10 & 1.11.
Run
Quickstart
-
Run:
docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --privileged -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui -
Open your browser to
http://<dockerd host ip>:9000
Bind mounting the Unix socket into the UI For Docker container is much more secure than exposing your docker daemon over TCP.
The --privileged flag is required for hosts using SELinux.
Specify socket to connect to Docker daemon
By default UI For Docker connects to the Docker daemon with/var/run/docker.sock. For this to work you need to bind mount the unix socket into the container with -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock.
You can use the --host, -H flags to change this socket:
# Connect to a tcp socket:
$ docker run -d -p 9000:9000 cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui -H tcp://127.0.0.1:2375
# Connect to another unix socket:
$ docker run -d -p 9000:9000 cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui -H unix:///path/to/docker.sock
Swarm support
Supported Swarm version: 1.2.3
You can access a specific view for you Swarm cluster by defining the --swarm flag:
# Connect to a tcp socket and enable Swarm:
$ docker run -d -p 9000:9000 cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui -H tcp://<SWARM_HOST>:<SWARM_PORT> --swarm
NOTE: Due to Swarm not exposing information in a machine readable way, the app is bound to a specific version of Swarm at the moment.
Change address/port UI For Docker is served on
UI For Docker listens on port 9000 by default. If you run UI For Docker inside a container then you can bind the container's internal port to any external address and port:
# Expose UI For Docker on 10.20.30.1:80
$ docker run -d -p 10.20.30.1:80:9000 --privileged -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui
Access a Docker engine protected via TLS
Ensure that you have access to the CA, the cert and the public key used to access your Docker engine.
These files will need to be named ca.pem, cert.pem and key.pem respectively. Store them somewhere on your disk and mount a volume containing these files inside the UI container:
$ docker run -d -p 9000:9000 cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui -v /path/to/certs:/certs -H https://my-docker-host.domain:2376 --tlsverify
You can also use the --tlscacert, --tlscert and --tlskey flags if you want to change the default path to the CA, certificate and key file respectively:
$ docker run -d -p 9000:9000 cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui -v /path/to/certs:/certs -H https://my-docker-host.domain:2376 --tlsverify --tlscacert /certs/myCa.pem --tlscert /certs/myCert.pem --tlskey /certs/myKey.pem
Note: Replace /path/to/certs to the path to the certificate files on your disk.
Hide containers with specific labels
You can hide specific containers in the containers view by using the --hide-label or -l options and specifying a label.
For example, take a container started with the label owner=acme:
$ docker run -d --label owner=acme nginx
You can hide it in the view by starting the ui with:
$ docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --privileged -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui -l owner=acme
Custom Docker registries support
You can specify the support of others registries than DockerHub by using the --registries or -r options and specifying a registry using the format REGISTRY_NAME=REGISTRY_ADDRESS.
For example, if I want the registry 'myCustomRegistry' pointing to myregistry.domain.com:5000 available in the UI:
$ docker run -d -p 9000:9000 --privileged -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock cloudinovasi/cloudinovasi-ui -r myCustomRegistry=myregistry.domain.com:5000
Available options
The following options are available for the ui-for-docker binary:
--host,-H: Docker daemon endpoint (default:"unix:///var/run/docker.sock")--bind,-p: Address and port to serve UI For Docker (default:":9000")--data,-d: Path to the data folder (default:".")--assets,-a: Path to the assets (default:".")--swarm,-s: Swarm cluster support (default:false)--registries,-r: Available registries in the UI (format REGISTRY_NAME=REGISTRY_ADDRESS)--tlsverify: TLS support (default:false)--tlscacert: Path to the CA (default/certs/ca.pem)--tlscert: Path to the TLS certificate file (default/certs/cert.pem)--tlskey: Path to the TLS key (default/certs/key.pem)--hide-label,-l: Hide containers with a specific label in the UI