* [misc] remove config arg from initialize * [misc] remove old tensor contrusctor * [plugin] add npu support for ddp * [pre-commit.ci] auto fixes from pre-commit.com hooks for more information, see https://pre-commit.ci * [devops] fix doc test ci * [test] fix test launch * [doc] update launch doc --------- Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| engine | ||
| kv_cache | ||
| quant | ||
| README.md | ||
| __init__.py | ||
README.md
🚀 Colossal-Inference
Table of Contents
Introduction
Colossal Inference is a module that contains colossal-ai designed inference framework, featuring high performance, steady and easy usability. Colossal Inference incorporated the advantages of the latest open-source inference systems, including LightLLM, TGI, vLLM, FasterTransformer and flash attention. while combining the design of Colossal AI, especially Shardformer, to reduce the learning curve for users.
Design
Colossal Inference is composed of three main components:
- High performance kernels and ops: which are inspired from existing libraries and modified correspondingly.
- Efficient memory management mechanism:which includes the key-value cache manager, allowing for zero memory waste during inference.
cache manager: serves as a memory manager to help manage the key-value cache, it integrates functions such as memory allocation, indexing and release.batch_infer_info: holds all essential elements of a batch inference, which is updated every batch.
- High-level inference engine combined with
Shardformer: it allows our inference framework to easily invoke and utilize various parallel methods.HybridEngine: it is a high level interface that integrates with shardformer, especially for multi-card (tensor parallel, pipline parallel) inference:modeling.llama.LlamaInferenceForwards: contains theforwardmethods for llama inference. (in this case : llama)policies.llama.LlamaModelInferPolicy: contains the policies forllamamodels, which is used to callshardformerand segmentate the model forward in tensor parallelism way.
Architecture of inference:
In this section we discuss how the colossal inference works and integrates with the Shardformer . The details can be found in our codes.
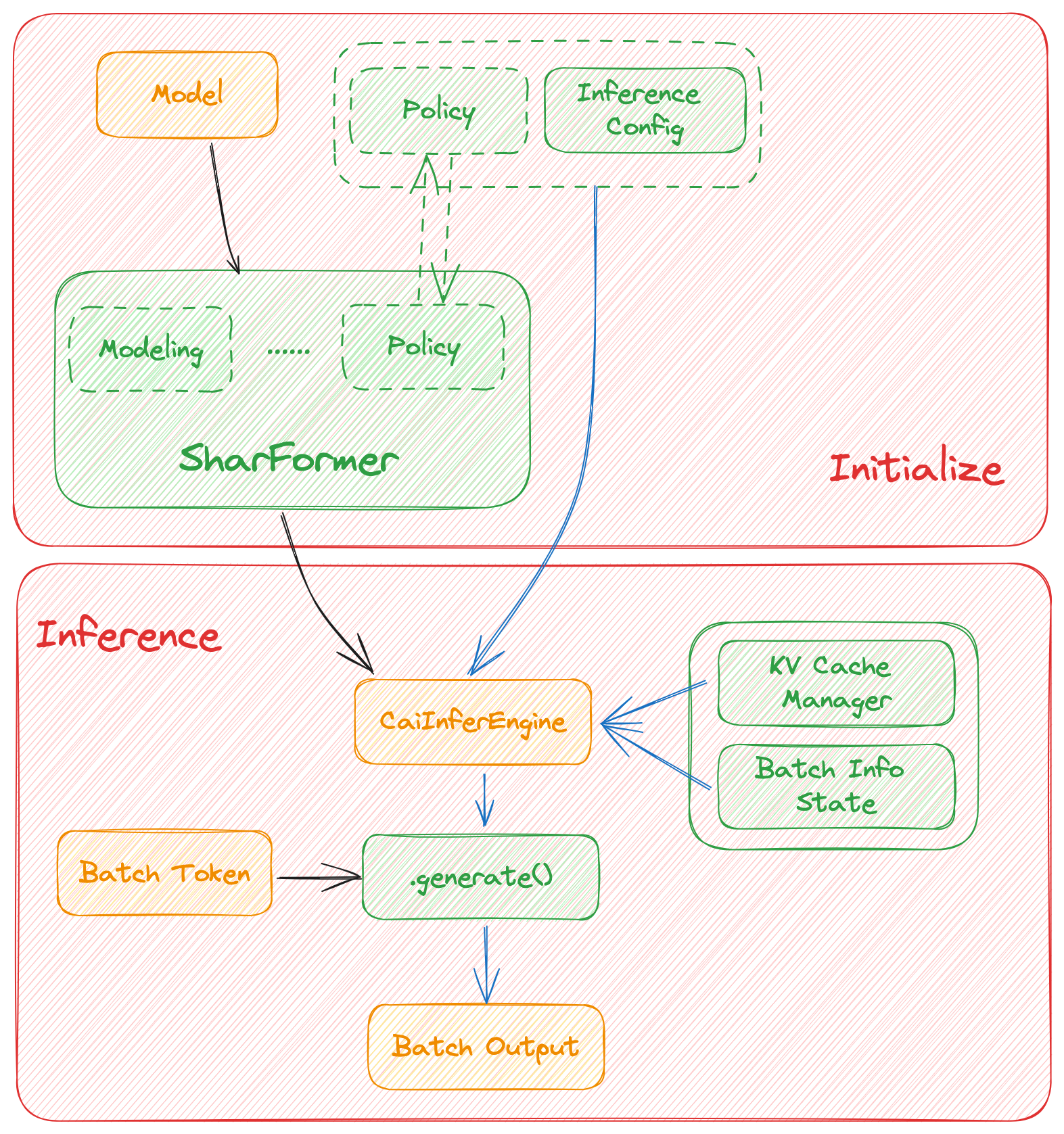
Roadmap of our implementation
- Design cache manager and batch infer state
- Design TpInference engine to integrates with
Shardformer - Register corresponding high-performance
kernelandops - Design policies and forwards (e.g.
LlamaandBloom)- policy
- context forward
- token forward
- support flash-decoding
- Support all models
- Llama
- Llama-2
- Bloom
- Chatglm2
- Quantization
- GPTQ
- SmoothQuant
- Benchmarking for all models
Get started
Installation
pip install -e .
Requirements
Install dependencies.
pip install -r requirements/requirements-infer.txt
# if you want use smoothquant quantization, please install torch-int
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/Guangxuan-Xiao/torch-int.git
cd torch-int
git checkout 65266db1eadba5ca78941b789803929e6e6c6856
pip install -r requirements.txt
source environment.sh
bash build_cutlass.sh
python setup.py install
Docker
You can use docker run to use docker container to set-up environment
# env: python==3.8, cuda 11.6, pytorch == 1.13.1 triton==2.0.0.dev20221202, vllm kernels support, flash-attention-2 kernels support
docker pull hpcaitech/colossalai-inference:v2
docker run -it --gpus all --name ANY_NAME -v $PWD:/workspace -w /workspace hpcaitech/colossalai-inference:v2 /bin/bash
# enter into docker container
cd /path/to/ColossalAI
pip install -e .
Usage
Quick start
example files are in
cd ColossalAI/examples
python hybrid_llama.py --path /path/to/model --tp_size 2 --pp_size 2 --batch_size 4 --max_input_size 32 --max_out_len 16 --micro_batch_size 2
Example
# import module
from colossalai.inference import CaiInferEngine
import colossalai
from transformers import LlamaForCausalLM, LlamaTokenizer
#launch distributed environment
colossalai.launch_from_torch()
# load original model and tokenizer
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained("/path/to/model")
tokenizer = LlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained("/path/to/model")
# generate token ids
input = ["Introduce a landmark in London","Introduce a landmark in Singapore"]
data = tokenizer(input, return_tensors='pt')
# set parallel parameters
tp_size=2
pp_size=2
max_output_len=32
micro_batch_size=1
# initial inference engine
engine = CaiInferEngine(
tp_size=tp_size,
pp_size=pp_size,
model=model,
max_output_len=max_output_len,
micro_batch_size=micro_batch_size,
)
# inference
output = engine.generate(data)
# get results
if dist.get_rank() == 0:
assert len(output[0]) == max_output_len, f"{len(output)}, {max_output_len}"
Performance
environment:
We conducted multiple benchmark tests to evaluate the performance. We compared the inference latency and throughputs between colossal-inference and original hugging-face torch fp16.
For various models, experiments were conducted using multiple batch sizes under the consistent model configuration of 7 billion(7b) parameters, 1024 input length, and 128 output length. The obtained results are as follows (due to time constraints, the evaluation has currently been performed solely on the A100 single GPU performance; multi-GPU performance will be addressed in the future):
Single GPU Performance:
Currently the stats below are calculated based on A100 (single GPU), and we calculate token latency based on average values of context-forward and decoding forward process, which means we combine both of processes to calculate token generation times. We are actively developing new features and methods to further optimize the performance of LLM models. Please stay tuned.
Tensor Parallelism Inference
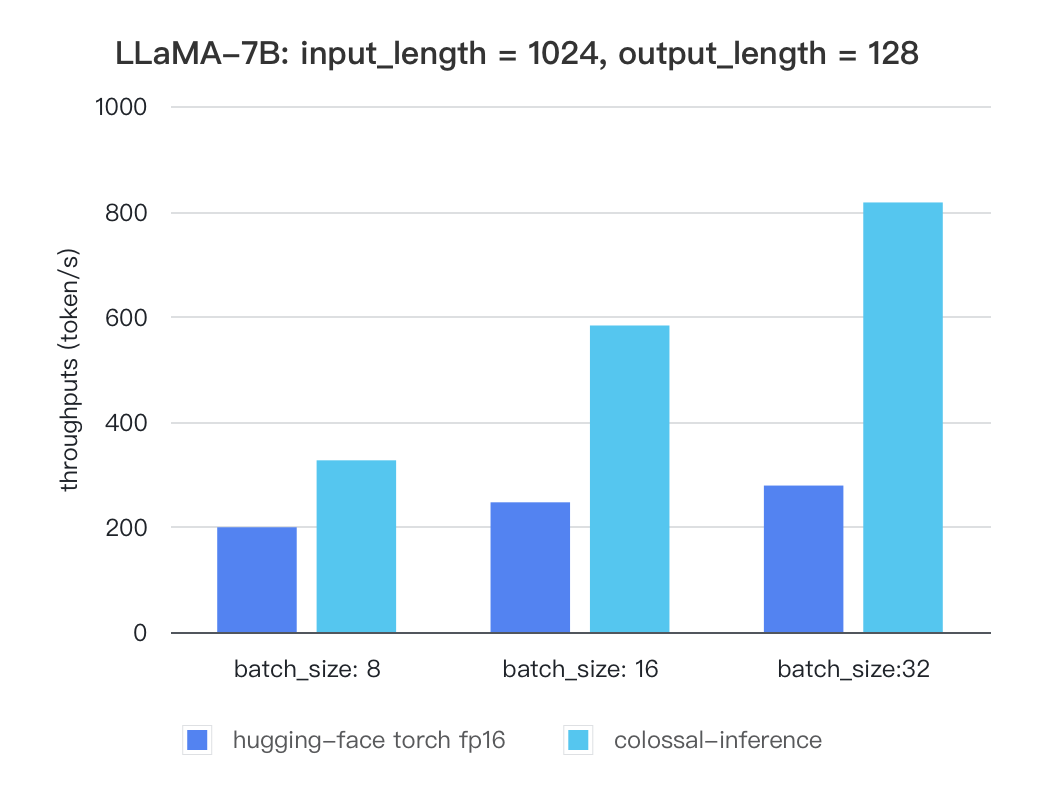
Llama
| batch_size | 8 | 16 | 32 |
|---|---|---|---|
| hugging-face torch fp16 | 199.12 | 246.56 | 278.4 |
| colossal-inference | 326.4 | 582.72 | 816.64 |
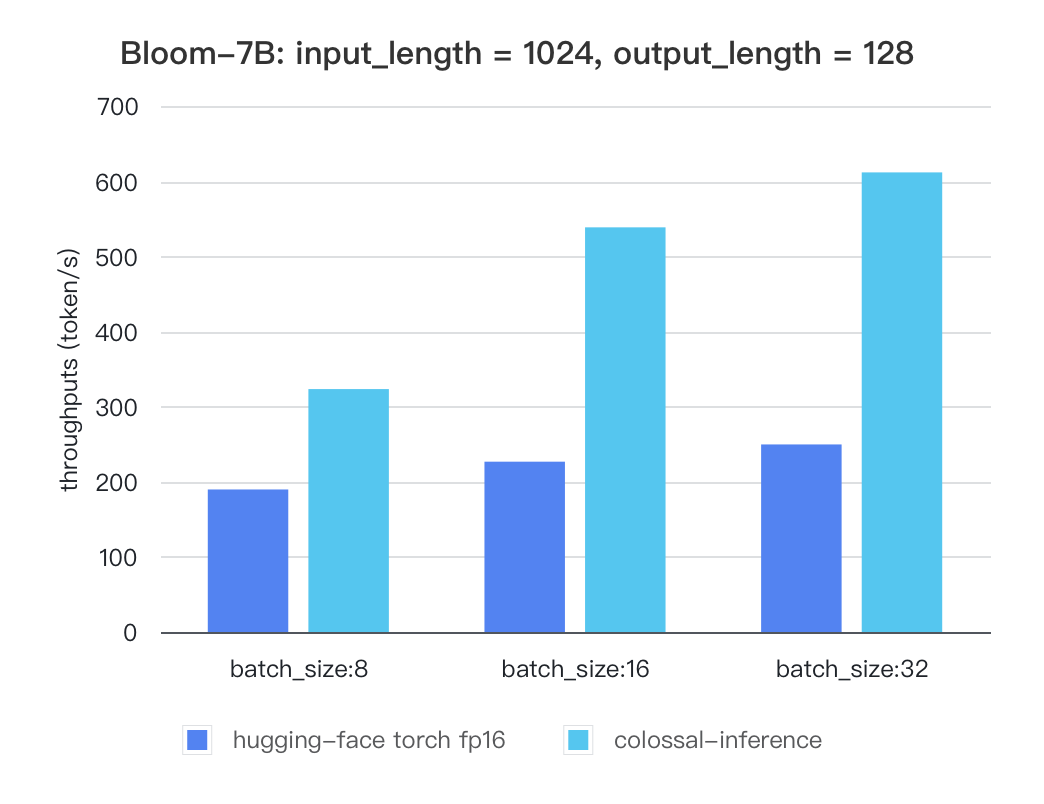
Bloom
| batch_size | 8 | 16 | 32 |
|---|---|---|---|
| hugging-face torch fp16 | 189.68 | 226.66 | 249.61 |
| colossal-inference | 323.28 | 538.52 | 611.64 |
Pipline Parallelism Inference
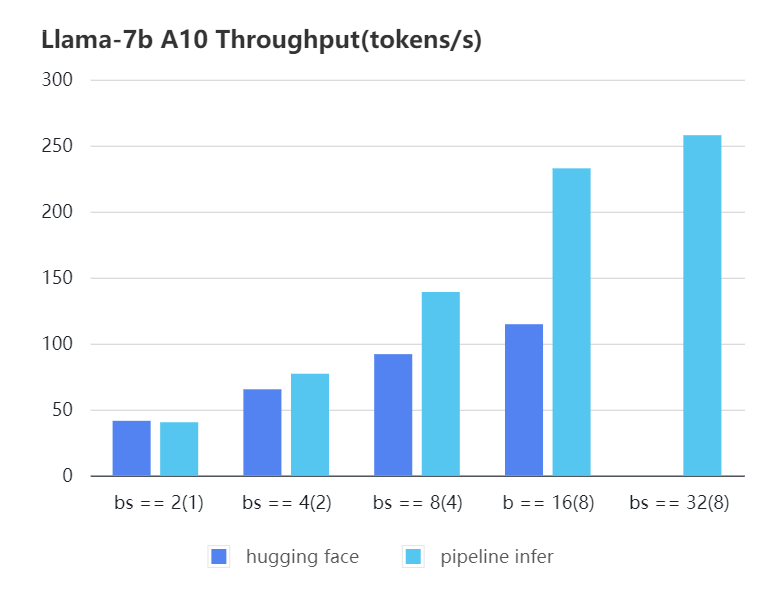
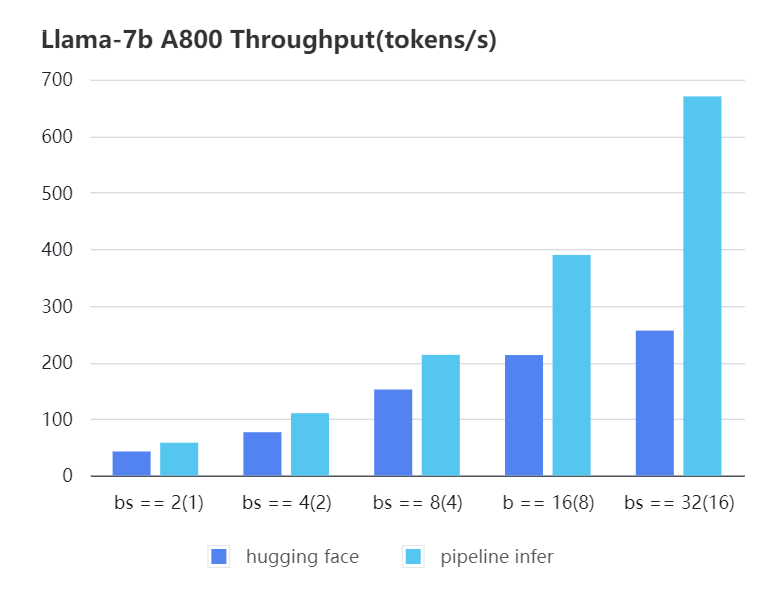
We conducted multiple benchmark tests to evaluate the performance. We compared the inference latency and throughputs between Pipeline Inference and hugging face pipeline. The test environment is 2 * A10, 20G / 2 * A800, 80G. We set input length=1024, output length=128.
A10 7b, fp16
| batch_size(micro_batch size) | 2(1) | 4(2) | 8(4) | 16(8) | 32(8) | 32(16) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipeline Inference | 40.35 | 77.10 | 139.03 | 232.70 | 257.81 | OOM |
| Hugging Face | 41.43 | 65.30 | 91.93 | 114.62 | OOM | OOM |
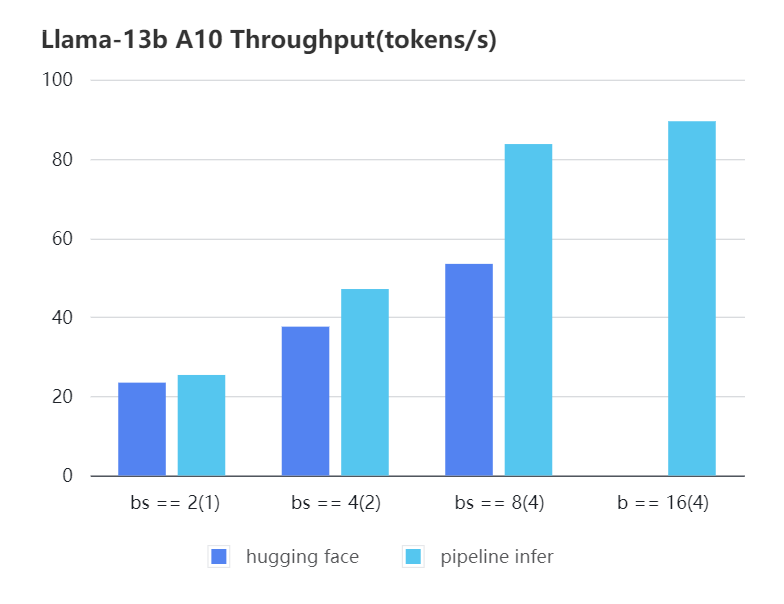
A10 13b, fp16
| batch_size(micro_batch size) | 2(1) | 4(2) | 8(4) | 16(4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipeline Inference | 25.39 | 47.09 | 83.7 | 89.46 |
| Hugging Face | 23.48 | 37.59 | 53.44 | OOM |
A800 7b, fp16
| batch_size(micro_batch size) | 2(1) | 4(2) | 8(4) | 16(8) | 32(16) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipeline Inference | 57.97 | 110.13 | 213.33 | 389.86 | 670.12 |
| Hugging Face | 42.44 | 76.5 | 151.97 | 212.88 | 256.13 |
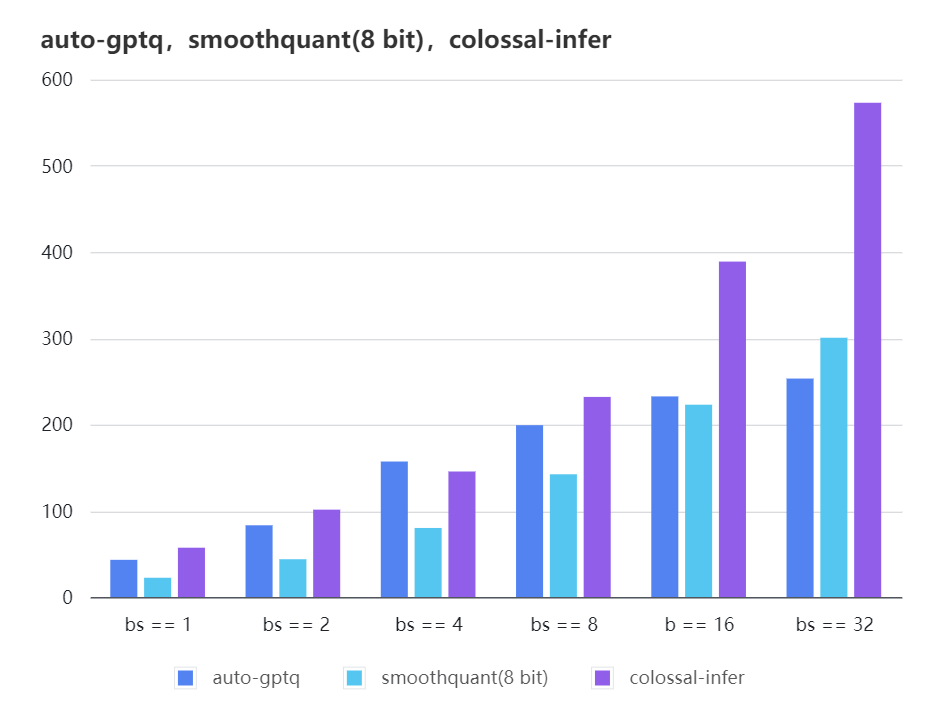
Quantization LLama
| batch_size | 8 | 16 | 32 |
|---|---|---|---|
| auto-gptq | 199.20 | 232.56 | 253.26 |
| smooth-quant | 142.28 | 222.96 | 300.59 |
| colossal-gptq | 231.98 | 388.87 | 573.03 |
The results of more models are coming soon!