* halfway * fix cross-PP-stage position id length diff bug * fix typo * fix typo * [pre-commit.ci] auto fixes from pre-commit.com hooks for more information, see https://pre-commit.ci * unified cross entropy func for all shardformer models * remove redundant lines * add basic ring attn; debug cross entropy * fwd bwd logic complete * fwd bwd logic complete; add experimental triton rescale * precision tests passed * precision tests passed * fix typos and remove misc files * [pre-commit.ci] auto fixes from pre-commit.com hooks for more information, see https://pre-commit.ci * add sp_mode to benchmark; fix varlen interface * update softmax_lse shape by new interface * change tester name * remove buffer clone; support packed seq layout * add varlen tests * fix typo * all tests passed * add dkv_group; fix mask * remove debug statements --------- Co-authored-by: Edenzzzz <wtan45@wisc.edu> Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| README.md | ||
| benchmark.sh | ||
| colossalai_zero.py | ||
| context.py | ||
| requirements.txt | ||
| run_clm.py | ||
| run_clm.sh | ||
| run_clm_synthetic.sh | ||
| test_ci.sh | ||
README.md
Train OPT model with Colossal-AI
OPT
Meta recently released Open Pretrained Transformer (OPT), a 175-Billion parameter AI language model, which stimulates AI programmers to perform various downstream tasks and application deployments.
The following example of Colossal-AI demonstrates fine-tuning causal Language Modelling at low cost.
We are using the pre-training weights of the OPT model provided by Hugging Face Hub on the raw WikiText-2 (no tokens were replaced before the tokenization). This training script is adapted from the HuggingFace Language Modelling examples.
Our Modifications
We adapt the OPT training code to ColossalAI by leveraging Gemini and ZeRO DDP.
🚀Quick Start for Tutorial
- Install the dependency
pip install datasets accelerate
- Run finetuning with synthetic datasets with one GPU
bash ./run_clm_synthetic.sh
- Run finetuning with 4 GPUs
bash ./run_clm_synthetic.sh 16 0 125m 4
Quick Start for Practical Use
You can launch training by using the following bash script
bash ./run_clm.sh <batch-size-per-gpu> <mem-cap> <model> <gpu-num>
- batch-size-per-gpu: number of samples fed to each GPU, default is 16
- mem-cap: limit memory usage within a value in GB, default is 0 (no limit)
- model: the size of the OPT model, default is
6.7b. Acceptable values include125m,350m,1.3b,2.7b,6.7,13b,30b,66b. For175b, you can request the pretrained weights from OPT weight downloading page. - gpu-num: the number of GPUs to use, default is 1.
It uses wikitext dataset.
To use synthetic dataset:
bash ./run_clm_synthetic.sh <batch-size-per-gpu> <mem-cap> <model> <gpu-num>
Remarkable Performance
On a single GPU, Colossal-AI’s automatic strategy provides remarkable performance gains from the ZeRO Offloading strategy by Microsoft DeepSpeed. Users can experience up to a 40% speedup, at a variety of model scales. However, when using a traditional deep learning training framework like PyTorch, a single GPU can no longer support the training of models at such a scale.
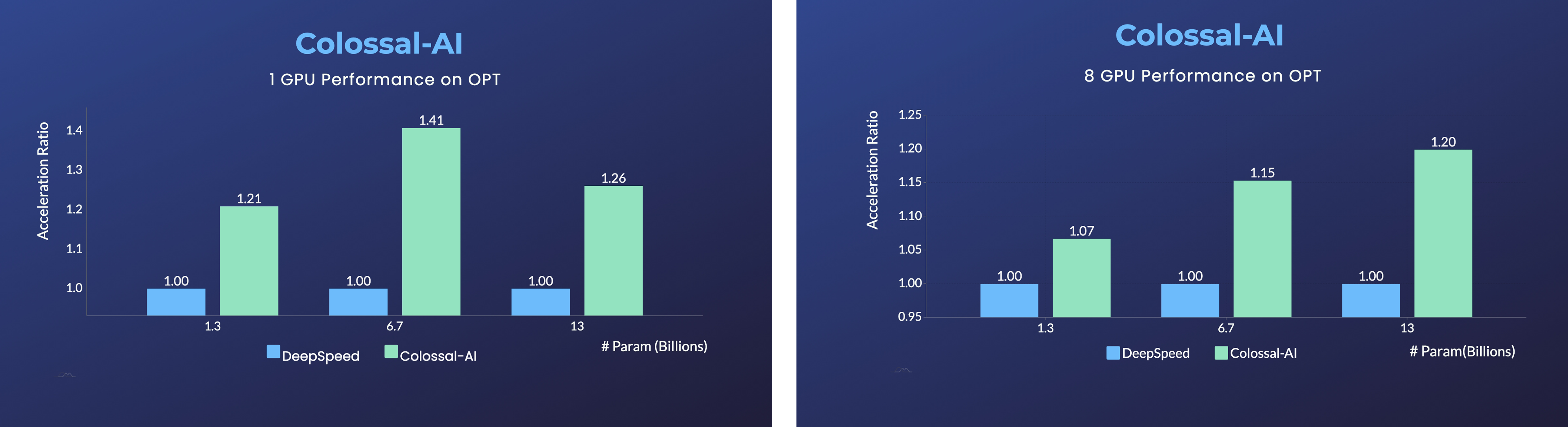
Adopting the distributed training strategy with 8 GPUs is as simple as adding a -nprocs 8 to the training command of Colossal-AI!
More details about behind the scenes can be found on the corresponding blog, and a detailed tutorial will be added in Documentation very soon.