# ColoDiffusion: Stable Diffusion with Colossal-AI
Acceleration of AIGC (AI-Generated Content) models such as [Stable Diffusion v1](https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion) and [Stable Diffusion v2](https://github.com/Stability-AI/stablediffusion).
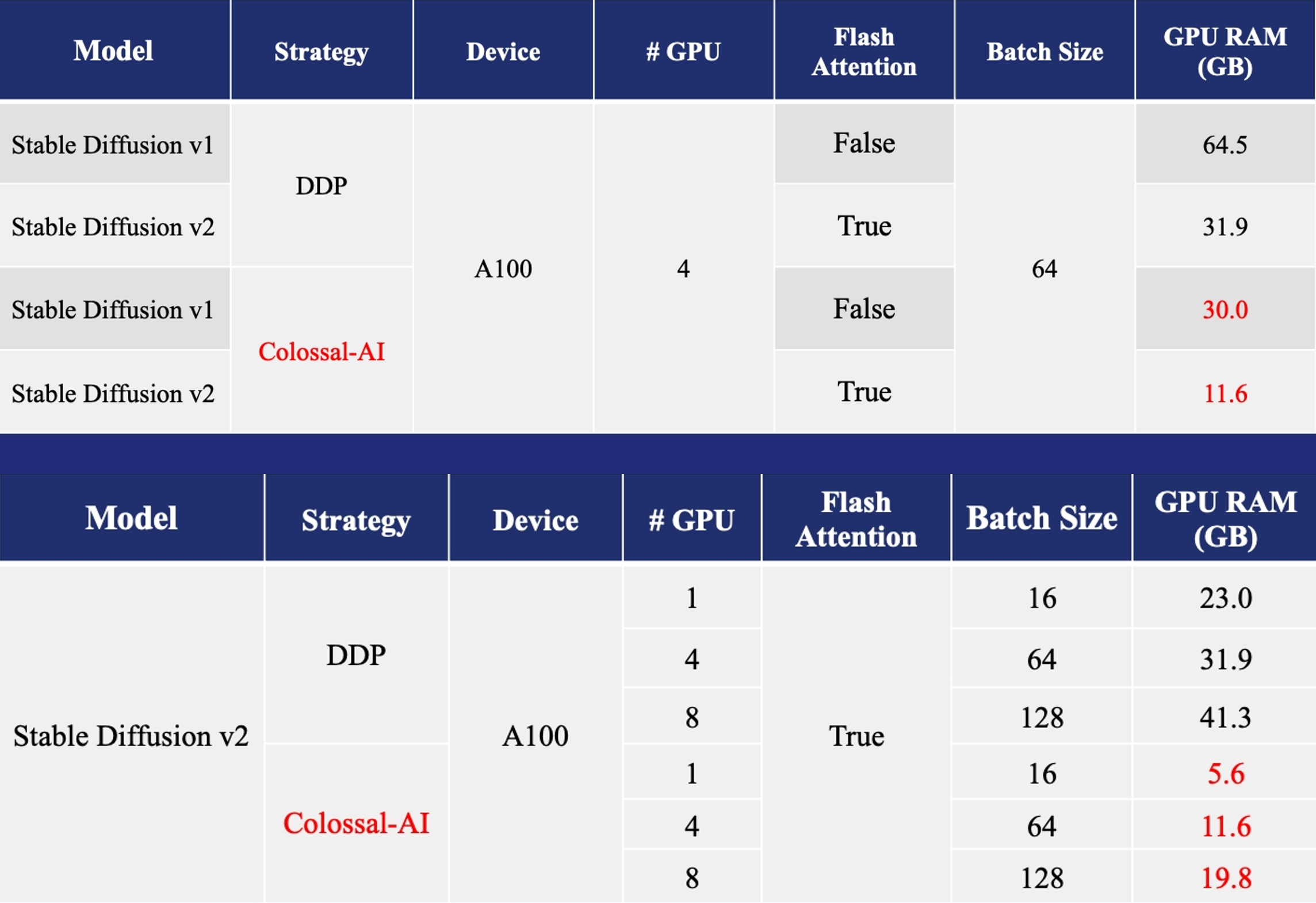
- [Training](https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI/tree/main/examples/images/diffusion): Reduce Stable Diffusion memory consumption by up to 5.6x and hardware cost by up to 46x (from A100 to RTX3060).

- [DreamBooth Fine-tuning](https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI/tree/main/examples/images/dreambooth): Personalize your model using just 3-5 images of the desired subject.

- [Inference](https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI/tree/main/examples/images/diffusion): Reduce inference GPU memory consumption by 2.5x.
More details can be found in our [blog of Stable Diffusion v1](https://www.hpc-ai.tech/blog/diffusion-pretraining-and-hardware-fine-tuning-can-be-almost-7x-cheaper) and [blog of Stable Diffusion v2](https://www.hpc-ai.tech/blog/colossal-ai-0-2-0).
## Roadmap
This project is in rapid development.
- [X] Train a stable diffusion model v1/v2 from scatch
- [X] Finetune a pretrained Stable diffusion v1 model
- [X] Inference a pretrained model using PyTorch
- [ ] Finetune a pretrained Stable diffusion v2 model
- [ ] Inference a pretrained model using TensoRT
## Installation
### Option #1: install from source
#### Step 1: Requirements
A suitable [conda](https://conda.io/) environment named `ldm` can be created
and activated with:
```
conda env create -f environment.yaml
conda activate ldm
```
You can also update an existing [latent diffusion](https://github.com/CompVis/latent-diffusion) environment by running
```
conda install pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch
pip install transformers diffusers invisible-watermark
```
#### Step 2:Install [Colossal-AI](https://colossalai.org/download/) From Our Official Website
##### From pip
For example, you can install v0.2.0 from our official website.
```
pip install colossalai
```
##### From source
```
git clone https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI.git
cd ColossalAI
# install colossalai
CUDA_EXT=1 pip install .
```
#### Step 3:Accelerate with flash attention by xformers(Optional)
```
pip install xformers
```
### Option #2: Use Docker
To use the stable diffusion Docker image, you can either build using the provided the [Dockerfile](./docker/Dockerfile) or pull a Docker image from our Docker hub.
```
# 1. build from dockerfile
cd docker
docker build -t hpcaitech/diffusion:0.2.0 .
# 2. pull from our docker hub
docker pull hpcaitech/diffusion:0.2.0
```
Once you have the image ready, you can launch the image with the following command:
```bash
########################
# On Your Host Machine #
########################
# make sure you start your image in the repository root directory
cd Colossal-AI
# run the docker container
docker run --rm \
-it --gpus all \
-v $PWD:/workspace \
-v :/data/scratch \
-v :/root/.cache/huggingface \
hpcaitech/diffusion:0.2.0 \
/bin/bash
########################
# Insider Container #
########################
# Once you have entered the docker container, go to the stable diffusion directory for training
cd examples/images/diffusion/
# start training with colossalai
bash train_colossalai.sh
```
It is important for you to configure your volume mapping in order to get the best training experience.
1. **Mandatory**, mount your prepared data to `/data/scratch` via `-v :/data/scratch`, where you need to replace `` with the actual data path on your machine.
2. **Recommended**, store the downloaded model weights to your host machine instead of the container directory via `-v :/root/.cache/huggingface`, where you need to repliace the `` with the actual path. In this way, you don't have to repeatedly download the pretrained weights for every `docker run`.
3. **Optional**, if you encounter any problem stating that shared memory is insufficient inside container, please add `-v /dev/shm:/dev/shm` to your `docker run` command.
## Download the model checkpoint from pretrained
### stable-diffusion-v2-base(Recommand)
```
wget https://huggingface.co/stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-base/resolve/main/512-base-ema.ckpt
```
### stable-diffusion-v1-4
```
git lfs install
git clone https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4
```
### stable-diffusion-v1-5 from runway
```
git lfs install
git clone https://huggingface.co/runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5
```
## Dataset
The dataSet is from [LAION-5B](https://laion.ai/blog/laion-5b/), the subset of [LAION](https://laion.ai/),
you should the change the `data.file_path` in the `config/train_colossalai.yaml`
## Training
We provide the script `train_colossalai.sh` to run the training task with colossalai,
and can also use `train_ddp.sh` to run the training task with ddp to compare.
In `train_colossalai.sh` the main command is:
```
python main.py --logdir /tmp/ --train --base configs/train_colossalai.yaml --ckpt 512-base-ema.ckpt
```
- You can change the `--logdir` to decide where to save the log information and the last checkpoint.
- You will find your ckpt in `logdir/checkpoints` or `logdir/diff_tb/version_0/checkpoints`
- You will find your train config yaml in `logdir/configs`
- You can add the `--ckpt` if you want to load the pretrained model, for example `512-base-ema.ckpt`
- You can change the `--base` to specify the path of config yaml
### Training config
You can change the trainging config in the yaml file
- devices: device number used for training, default 8
- max_epochs: max training epochs, default 2
- precision: the precision type used in training, default 16 (fp16), you must use fp16 if you want to apply colossalai
- more information about the configuration of ColossalAIStrategy can be found [here](https://pytorch-lightning.readthedocs.io/en/latest/advanced/model_parallel.html#colossal-ai)
## Finetune Example
### Training on Teyvat Datasets
We provide the finetuning example on [Teyvat](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Fazzie/Teyvat) dataset, which is create by BLIP generated captions.
You can run by config `configs/Teyvat/train_colossalai_teyvat.yaml`
```
python main.py --logdir /tmp/ -t -b configs/Teyvat/train_colossalai_teyvat.yaml
```
## Inference
you can get yout training last.ckpt and train config.yaml in your `--logdir`, and run by
```
python scripts/txt2img.py --prompt "a photograph of an astronaut riding a horse" --plms
--outdir ./output \
--ckpt path/to/logdir/checkpoints/last.ckpt \
--config /path/to/logdir/configs/project.yaml \
```
```commandline
usage: txt2img.py [-h] [--prompt [PROMPT]] [--outdir [OUTDIR]] [--skip_grid] [--skip_save] [--ddim_steps DDIM_STEPS] [--plms] [--laion400m] [--fixed_code] [--ddim_eta DDIM_ETA]
[--n_iter N_ITER] [--H H] [--W W] [--C C] [--f F] [--n_samples N_SAMPLES] [--n_rows N_ROWS] [--scale SCALE] [--from-file FROM_FILE] [--config CONFIG] [--ckpt CKPT]
[--seed SEED] [--precision {full,autocast}]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--prompt [PROMPT] the prompt to render
--outdir [OUTDIR] dir to write results to
--skip_grid do not save a grid, only individual samples. Helpful when evaluating lots of samples
--skip_save do not save individual samples. For speed measurements.
--ddim_steps DDIM_STEPS
number of ddim sampling steps
--plms use plms sampling
--laion400m uses the LAION400M model
--fixed_code if enabled, uses the same starting code across samples
--ddim_eta DDIM_ETA ddim eta (eta=0.0 corresponds to deterministic sampling
--n_iter N_ITER sample this often
--H H image height, in pixel space
--W W image width, in pixel space
--C C latent channels
--f F downsampling factor
--n_samples N_SAMPLES
how many samples to produce for each given prompt. A.k.a. batch size
--n_rows N_ROWS rows in the grid (default: n_samples)
--scale SCALE unconditional guidance scale: eps = eps(x, empty) + scale * (eps(x, cond) - eps(x, empty))
--from-file FROM_FILE
if specified, load prompts from this file
--config CONFIG path to config which constructs model
--ckpt CKPT path to checkpoint of model
--seed SEED the seed (for reproducible sampling)
--use_int8 whether to use quantization method
--precision {full,autocast}
evaluate at this precision
```
## Comments
- Our codebase for the diffusion models builds heavily on [OpenAI's ADM codebase](https://github.com/openai/guided-diffusion)
, [lucidrains](https://github.com/lucidrains/denoising-diffusion-pytorch),
[Stable Diffusion](https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion), [Lightning](https://github.com/Lightning-AI/lightning) and [Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/CompVis/stable-diffusion).
Thanks for open-sourcing!
- The implementation of the transformer encoder is from [x-transformers](https://github.com/lucidrains/x-transformers) by [lucidrains](https://github.com/lucidrains?tab=repositories).
- The implementation of [flash attention](https://github.com/HazyResearch/flash-attention) is from [HazyResearch](https://github.com/HazyResearch).
## BibTeX
```
@article{bian2021colossal,
title={Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training},
author={Bian, Zhengda and Liu, Hongxin and Wang, Boxiang and Huang, Haichen and Li, Yongbin and Wang, Chuanrui and Cui, Fan and You, Yang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.14883},
year={2021}
}
@misc{rombach2021highresolution,
title={High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models},
author={Robin Rombach and Andreas Blattmann and Dominik Lorenz and Patrick Esser and Björn Ommer},
year={2021},
eprint={2112.10752},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
@article{dao2022flashattention,
title={FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness},
author={Dao, Tri and Fu, Daniel Y. and Ermon, Stefano and Rudra, Atri and R{\'e}, Christopher},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.14135},
year={2022}
}
```



