# Pretraining LLaMA-1/2: best practices for building LLaMA-1/2-like base models
### LLaMA2
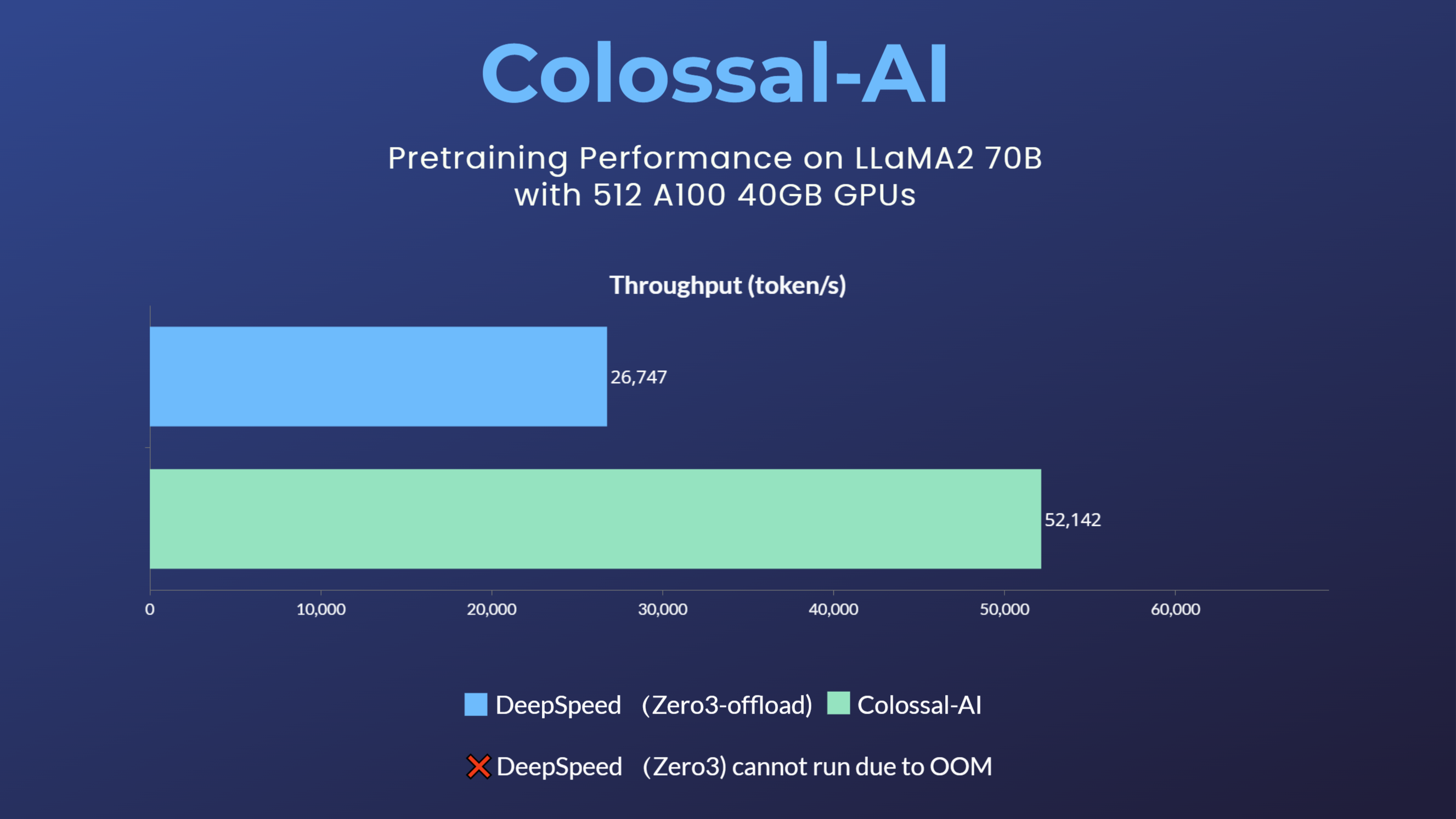
- 70 billion parameter LLaMA2 model training accelerated by 195%
[[code]](https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI/tree/main/examples/language/llama2)
[[blog]](https://www.hpc-ai.tech/blog/70b-llama2-training)
### LLaMA1
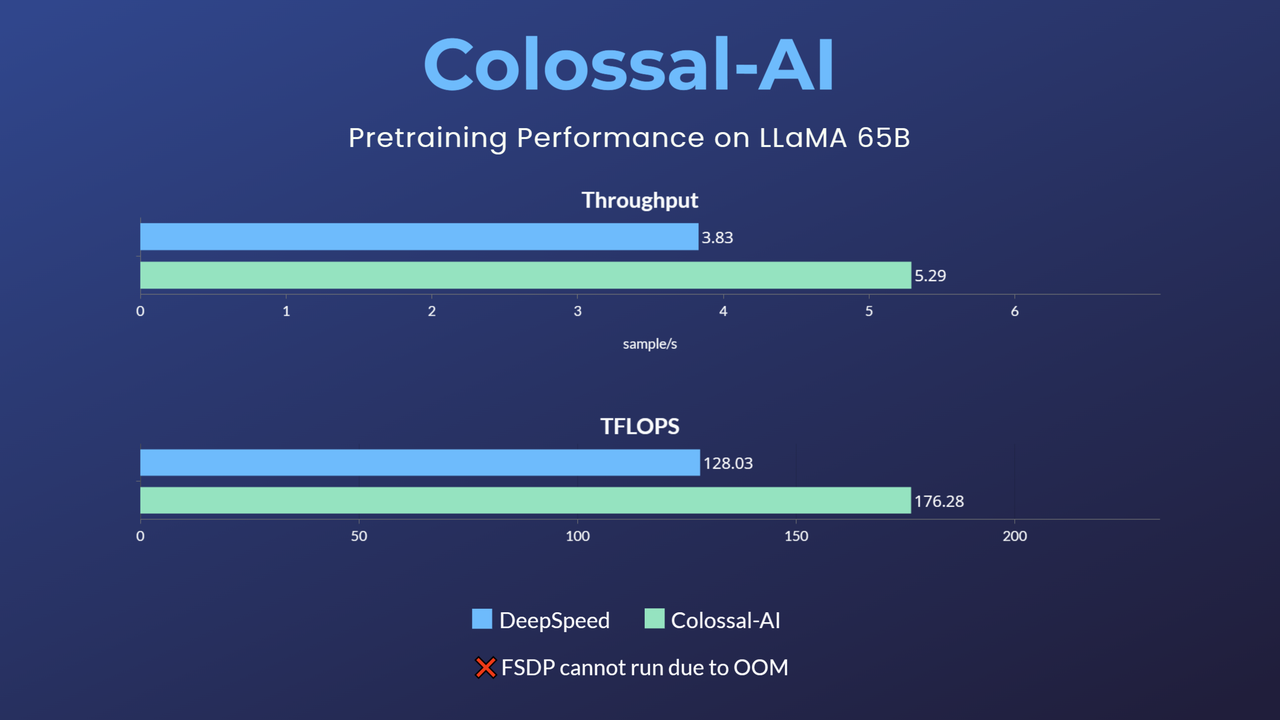
- 65-billion-parameter large model pretraining accelerated by 38%
[[code]](https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI/tree/example/llama/examples/language/llama)
[[blog]](https://www.hpc-ai.tech/blog/large-model-pretraining)
## Dataset
Different from the original LLaMA, we use [RedPajama](https://www.together.xyz/blog/redpajama) dataset, which is a reproduction of the LLaMA training dataset containing over 1.2 trillion tokens. The full dataset is ~5TB unzipped on disk and ~3TB to download compressed.
A smaller, more consumable random sample can be downloaded through [Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/datasets/togethercomputer/RedPajama-Data-1T). If you just want to try out the pretraining script, you can use a 1B-token sample subset of RedPajama, which is available at [Hugging Face](https://huggingface.co/datasets/togethercomputer/RedPajama-Data-1T-Sample).
RedPajama-Data-1T consists of seven data slices:
| | RedPajama | LLaMA |
|---------------|--------------|---------------|
| CommonCrawl | 878 billion | 852 billion |
| C4 | 175 billion | 190 billion |
| Github | 59 billion | 100 billion |
| Books | 26 billion | 25 billion |
| ArXiv | 28 billion | 33 billion |
| Wikipedia | 24 billion | 25 billion |
| StackExchange | 20 billion | 27 billion |
| Total | 1.2 trillion | 1.25 trillion |
## Training
We follow the hyperparameter settings from the original LLaMA paper. We use AdamW with $beta1=0.9$ and $beta2=0.95$. We use a cosine learning rate schedule, such that the final learning rate is equal to 10% of the maximal learning rate. We use a weight decay of 0.1 and gradient clipping of 1.0. We use 2,000 warmup steps.
| params | learning rate | batch size |
|--------|---------------|------------|
| 6.7B | 3.0e-4 | 4M |
| 13.0B | 3.0e-4 | 4M |
| 32.5B | 1.5e-4 | 4M |
| 65.2B | 1.5e-4 | 4M |
## Usage
### 1. Installation
Please install the latest ColossalAI from source.
```bash
CUDA_EXT=1 pip install -U git+https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI
```
Then install other dependencies.
```bash
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
Additionally, we recommend you to use torch 1.13.1. We've tested our code on torch 1.13.1 and found it's compatible with our code and flash attention.
### 2. Download the dataset
The dataset can be automatically downloaded by using `huggingface/datasets`. You can specify the dataset path by `-d` or `--dataset`. The default dataset is `togethercomputer/RedPajama-Data-1T-Sample`.
### 3. Command line arguments
Yon can use colossalai run to launch multi-nodes training:
```bash
colossalai run --nproc_per_node YOUR_GPU_PER_NODE --hostfile YOUR_HOST_FILE \
pretrain.py --OTHER_CONFIGURATIONS
```
Here is a sample hostfile:
```text
hostname1
hostname2
hostname3
hostname4
```
Make sure master node can access all nodes (including itself) by ssh without password.
Here is details about CLI arguments:
- Model configuration: `-c`, `--config`. `7b`, `13b`, `30b` and `65b` are supported for LLaMA-1, `7b`, `13b`, and `70b` are supported for LLaMA-2.
- Booster plugin: `-p`, `--plugin`. `gemini`, `gemini_auto`, `zero2` and `zero2_cpu` are supported. For more details, please refer to [Booster plugins](https://colossalai.org/docs/basics/booster_plugins).
- Dataset path: `-d`, `--dataset`. The default dataset is `togethercomputer/RedPajama-Data-1T-Sample`. It support any dataset from `datasets` with the same data format as RedPajama.
- Number of epochs: `-e`, `--num_epochs`. The default value is 1.
- Local batch size: `-b`, `--batch_size`. Batch size per GPU. The default value is 2.
- Learning rate: `--lr`. The default value is 3e-4.
- Weight decay: `-w`, `--weight_decay`. The default value is 0.1.
- Warmup steps: `-s`, `--warmup_steps`. The default value is 2000.
- Gradient checkpointing: `-g`, `--gradient_checkpoint`. The default value is `False`. This saves memory at the cost of speed. You'd better enable this option when training with a large batch size.
- Max length: `-l`, `--max_length`. The default value is 4096.
- Mixed precision: `-x`, `--mixed_precision`. The default value is "fp16". "fp16" and "bf16" are supported.
- Save interval: `-i`, `--save_interval`. The interval (steps) of saving checkpoints. The default value is 1000.
- Checkpoint directory: `-o`, `--save_dir`. The directoty path to save checkpoints. The default value is `checkpoint`.
- Checkpoint to load: `-f`, `--load`. The checkpoint path to load. The default value is `None`.
- Gradient clipping: `--gradient_clipping`. The default value is 1.0.
- Tensorboard log directory: `-t`, `--tensorboard_dir`. The directory path to save tensorboard logs. The default value is `tb_logs`.
- Flash attention: `-a`, `--flash_attention`. If you want to use flash attention, you must install `flash-attn`. The default value is `False`. This is helpful to accelerate training while saving memory. We recommend you always use flash attention.
### 4. Shell Script Examples
For your convenience, we provide some shell scripts to run benchmark with various configurations.
You can find them in `scripts/benchmark_7B` and `scripts/benchmark_70B` directory. The main command should be in the format of:
```bash
colossalai run --nproc_per_node YOUR_GPU_PER_NODE --hostfile YOUR_HOST_FILE \
benchmark.py --OTHER_CONFIGURATIONS
```
Here we will show an example of how to run training
llama pretraining with `gemini, batch_size=16, sequence_length=4096, gradient_checkpoint=True, flash_attn=True`.
#### a. Running environment
This experiment was performed on 4 computing nodes with 32 A800 GPUs in total for LLaMA-1 65B. The nodes are
connected with RDMA and GPUs within one node are fully connected with NVLink.
#### b. Running command
```bash
cd scripts/benchmark_7B
```
First, put your host file (`hosts.txt`) in this directory with your real host ip or host name.
Here is a sample `hosts.txt`:
```text
hostname1
hostname2
hostname3
hostname4
```
Then add environment variables to script if needed.
Finally, run the following command to start training:
```bash
bash gemini.sh
```
If you encounter out-of-memory(OOM) error during training with script `gemini.sh`, changing to script `gemini_auto.sh` might be a solution, since gemini_auto will set a upper limit on GPU memory usage through offloading part of the model parameters and optimizer states back to CPU memory. But there's a trade-off: `gemini_auto.sh` will be a bit slower, since more data are transmitted between CPU and GPU.
#### c. Results
If you run the above command successfully, you will get the following results:
`max memory usage: 55491.10 MB, throughput: 24.26 samples/s, TFLOPS/GPU: 167.43`.
## Reference
```
@article{bian2021colossal,
title={Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System For Large-Scale Parallel Training},
author={Bian, Zhengda and Liu, Hongxin and Wang, Boxiang and Huang, Haichen and Li, Yongbin and Wang, Chuanrui and Cui, Fan and You, Yang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.14883},
year={2021}
}
```
```bibtex
@software{openlm2023openllama,
author = {Geng, Xinyang and Liu, Hao},
title = {OpenLLaMA: An Open Reproduction of LLaMA},
month = May,
year = 2023,
url = {https://github.com/openlm-research/open_llama}
}
```
```bibtex
@software{together2023redpajama,
author = {Together Computer},
title = {RedPajama-Data: An Open Source Recipe to Reproduce LLaMA training dataset},
month = April,
year = 2023,
url = {https://github.com/togethercomputer/RedPajama-Data}
}
```
```bibtex
@article{touvron2023llama,
title={Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models},
author={Touvron, Hugo and Lavril, Thibaut and Izacard, Gautier and Martinet, Xavier and Lachaux, Marie-Anne and Lacroix, Timoth{\'e}e and Rozi{\`e}re, Baptiste and Goyal, Naman and Hambro, Eric and Azhar, Faisal and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971},
year={2023}
}
```


