mirror of https://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI
[inference] update readme (#5051)
* update readme * update readme * fix architecture * fix table * fix tablefeature/inference-refactor
parent
361cf63cb0
commit
5446fb70c4
|
|
@ -1,6 +1,14 @@
|
|||
# 🚀 Colossal-Inference
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of contents
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of Contents
|
||||
- [💡 Introduction](#introduction)
|
||||
- [🔗 Design](#design)
|
||||
- [🔨 Usage](#usage)
|
||||
- [Quick start](#quick-start)
|
||||
- [Example](#example)
|
||||
|
||||
- [📊 Performance](#performance)
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -15,15 +23,16 @@ Colossal Inference is composed of two main components:
|
|||
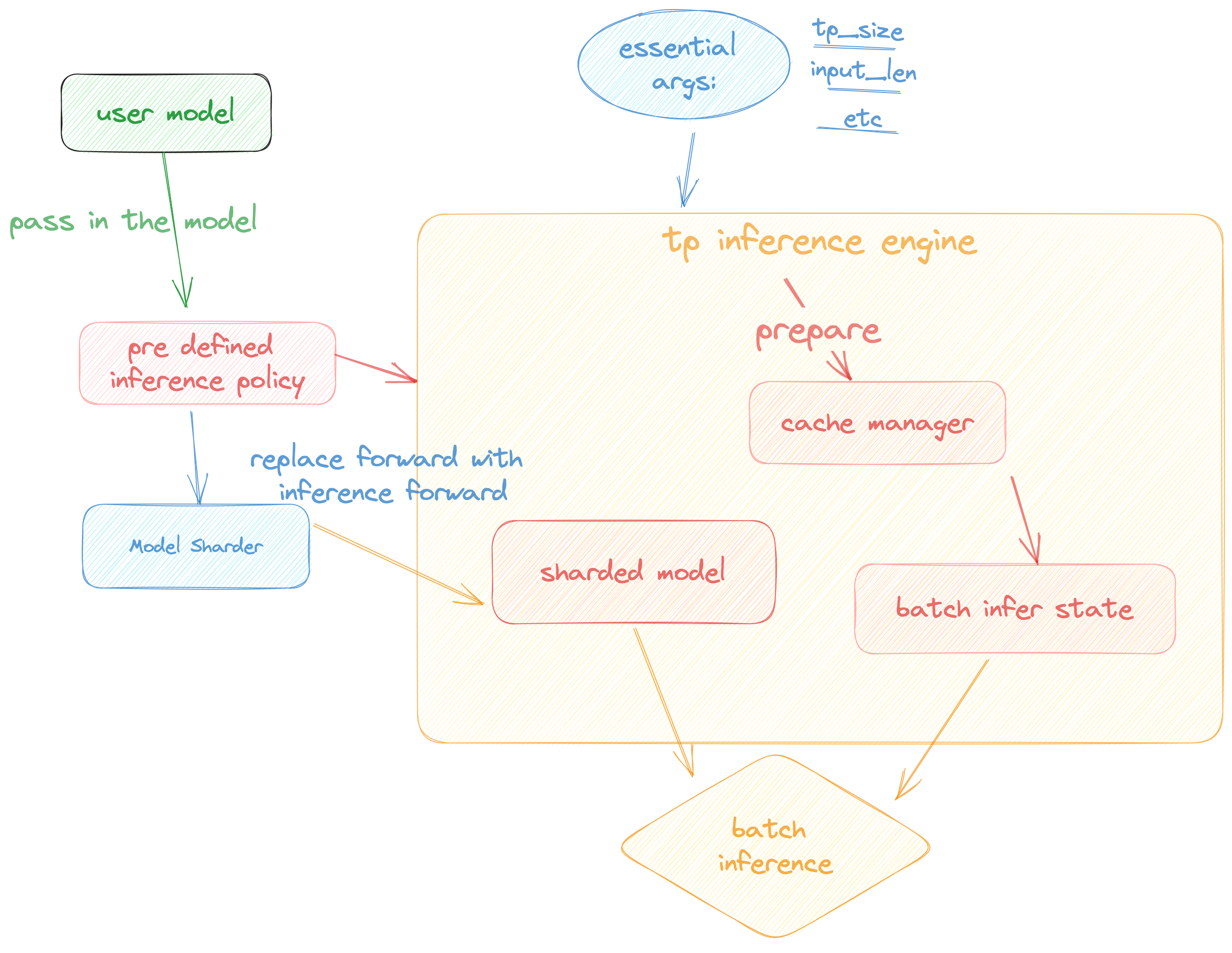
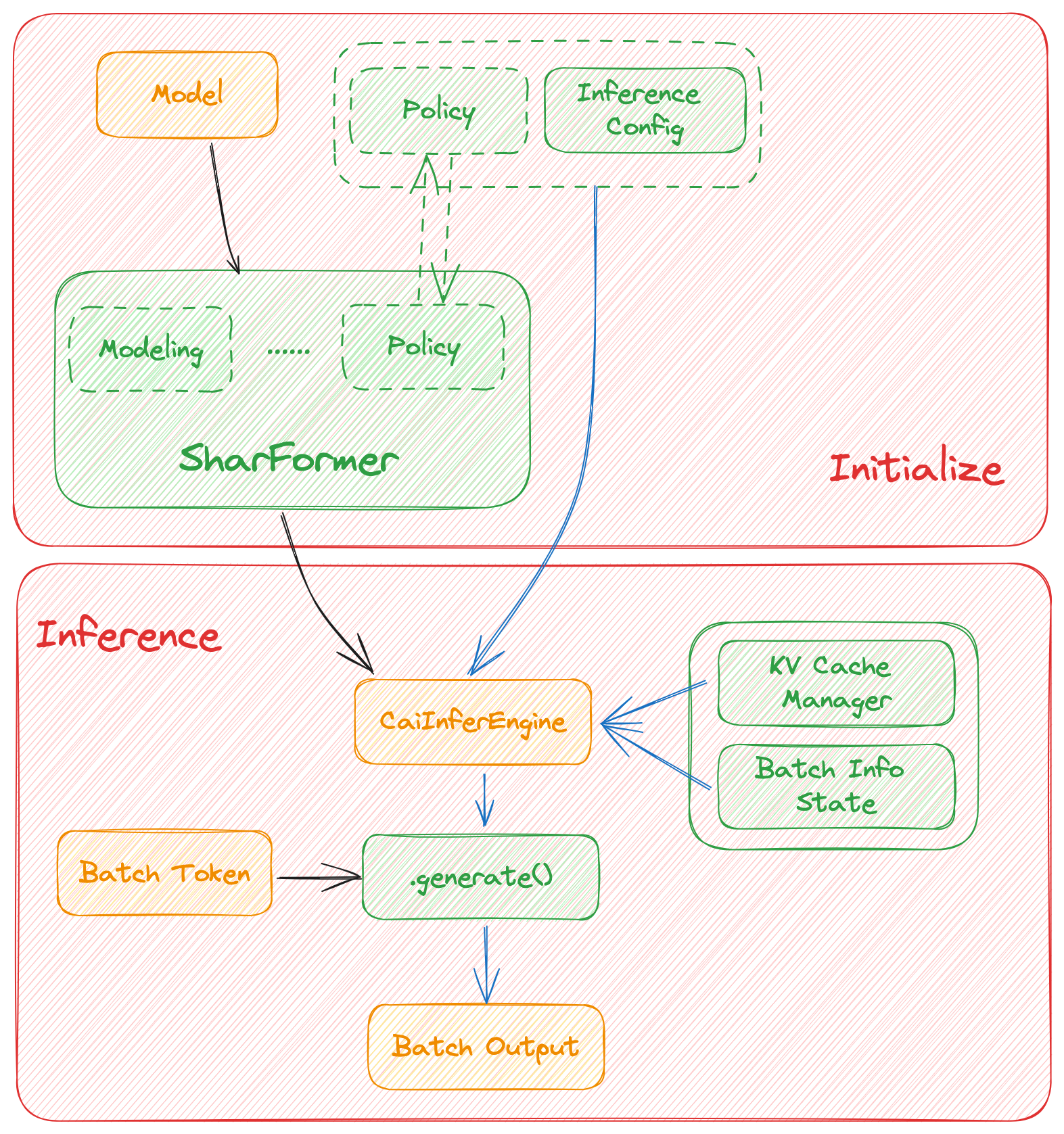
1. `cache manager`: serves as a memory manager to help manage the key-value cache, it integrates functions such as memory allocation, indexing and release.
|
||||
2. `batch_infer_info`: holds all essential elements of a batch inference, which is updated every batch.
|
||||
3. High-level inference engine combined with `Shardformer`: it allows our inference framework to easily invoke and utilize various parallel methods.
|
||||
1. `engine.TPInferEngine`: it is a high level interface that integrates with shardformer, especially for multi-card (tensor parallel) inference:
|
||||
1. `HybridEngine`: it is a high level interface that integrates with shardformer, especially for multi-card (tensor parallel, pipline parallel) inference:
|
||||
2. `modeling.llama.LlamaInferenceForwards`: contains the `forward` methods for llama inference. (in this case : llama)
|
||||
3. `policies.llama.LlamaModelInferPolicy` : contains the policies for `llama` models, which is used to call `shardformer` and segmentate the model forward in tensor parallelism way.
|
||||
|
||||
## Pipeline of inference:
|
||||
|
||||
## Architecture of inference:
|
||||
|
||||
In this section we discuss how the colossal inference works and integrates with the `Shardformer` . The details can be found in our codes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Roadmap of our implementation
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,12 +44,14 @@ In this section we discuss how the colossal inference works and integrates with
|
|||
- [x] context forward
|
||||
- [x] token forward
|
||||
- [x] support flash-decoding
|
||||
- [ ] Replace the kernels with `faster-transformer` in token-forward stage
|
||||
- [ ] Support all models
|
||||
- [x] Llama
|
||||
- [x] Llama-2
|
||||
- [x] Bloom
|
||||
- [x] Chatglm2
|
||||
- [ ] Quantization
|
||||
- [x] GPTQ
|
||||
- [x] SmoothQuant
|
||||
- [ ] Benchmarking for all models
|
||||
|
||||
## Get started
|
||||
|
|
@ -64,12 +75,12 @@ triton
|
|||
flash-attention
|
||||
|
||||
# install lightllm since we depend on lightllm triton kernels
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ModelTC/lightllm
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ModelTC/lightllm
|
||||
cd lightllm
|
||||
git checkout 28c1267cfca536b7b4f28e921e03de735b003039
|
||||
pip3 install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
# also, install xformers from source:
|
||||
# also, install xformers from source:
|
||||
pip install ninja
|
||||
# Set TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST if running and building on different GPU types
|
||||
pip install -v -U git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers.git@main#egg=xformers
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,18 +101,29 @@ cd /path/to/CollossalAI
|
|||
pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
# install lightllm
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ModelTC/lightllm
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ModelTC/lightllm
|
||||
cd lightllm
|
||||
git checkout 28c1267cfca536b7b4f28e921e03de735b003039
|
||||
pip3 install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
# install xformers from source
|
||||
# install xformers from source
|
||||
pip install ninja
|
||||
# Set TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST if running and building on different GPU types
|
||||
pip install -v -U git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers.git@main#egg=xformers
|
||||
pip install -v -U git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers.git@main#egg=xformers
|
||||
|
||||
# for gptq quantization
|
||||
pip install auto-gptq
|
||||
|
||||
# for smoothquant quantization
|
||||
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/Guangxuan-Xiao/torch-int.git
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
source environment.sh
|
||||
bash build_cutlass.sh
|
||||
python setup.py install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Dive into fast-inference!
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
### Quick start
|
||||
|
||||
example files are in
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -110,6 +132,44 @@ cd colossalai.examples
|
|||
python xx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from colossalai.inference import PPInferEngine
|
||||
from colossalai.inference.pipeline.policies import LlamaModelInferPolicy
|
||||
import colossalai
|
||||
from transformers import LlamaForCausalLM, LlamaTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
colossalai.launch_from_torch(config={})
|
||||
|
||||
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained("/path/to/model")
|
||||
tokenizer = LlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained("/path/to/model")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
input = ["Introduce a landmark in London","Introduce a landmark in Singapore"]
|
||||
data = tokenizer(input, return_tensors='pt')
|
||||
output = inferengine.inference(data.to('cuda'))
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(output))
|
||||
|
||||
tp_size=2
|
||||
pp_size=2
|
||||
max_output_len=32
|
||||
micro_batch_size=1
|
||||
|
||||
engine = CaiInferEngine(
|
||||
tp_size=tp_size,
|
||||
pp_size=pp_size,
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
model_policy=LlamaModelInferPolicy(),
|
||||
max_output_len=max_output_len,
|
||||
micro_batch_size=micro_batch_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
output = engine.inference(data)
|
||||
if dist.get_rank() == 0:
|
||||
assert len(output[0]) == max_output_len, f"{len(output)}, {max_output_len}"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Performance
|
||||
|
||||
### environment:
|
||||
|
|
@ -122,7 +182,9 @@ For various models, experiments were conducted using multiple batch sizes under
|
|||
|
||||
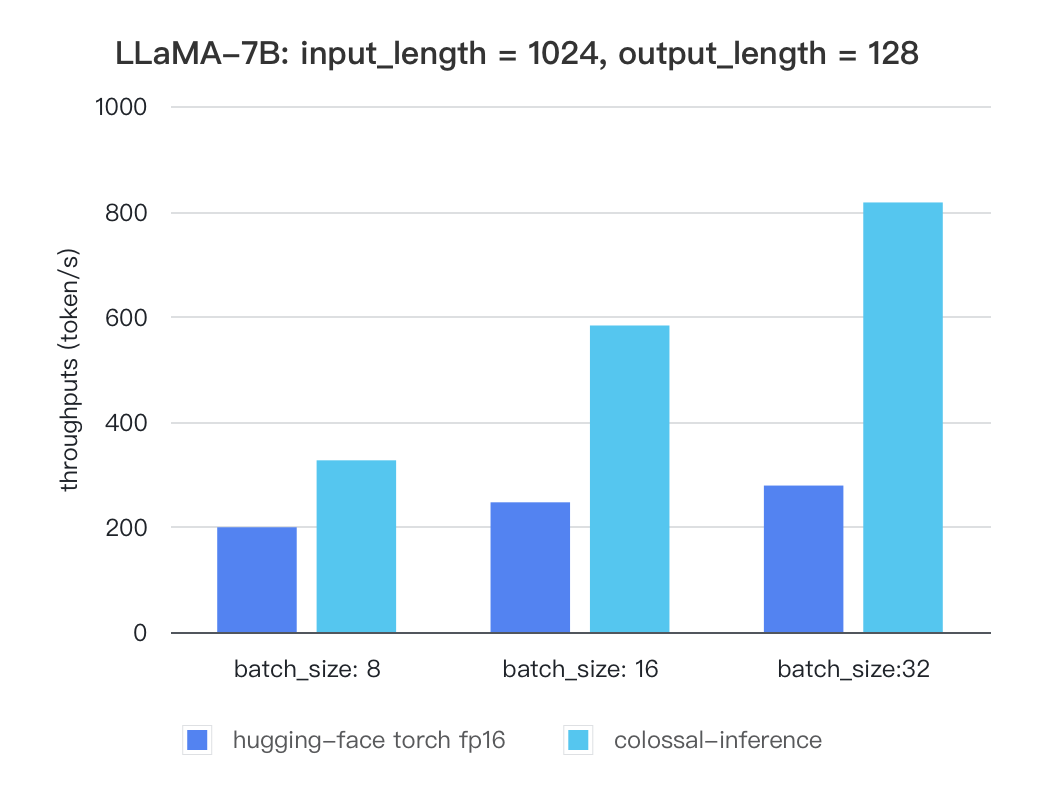
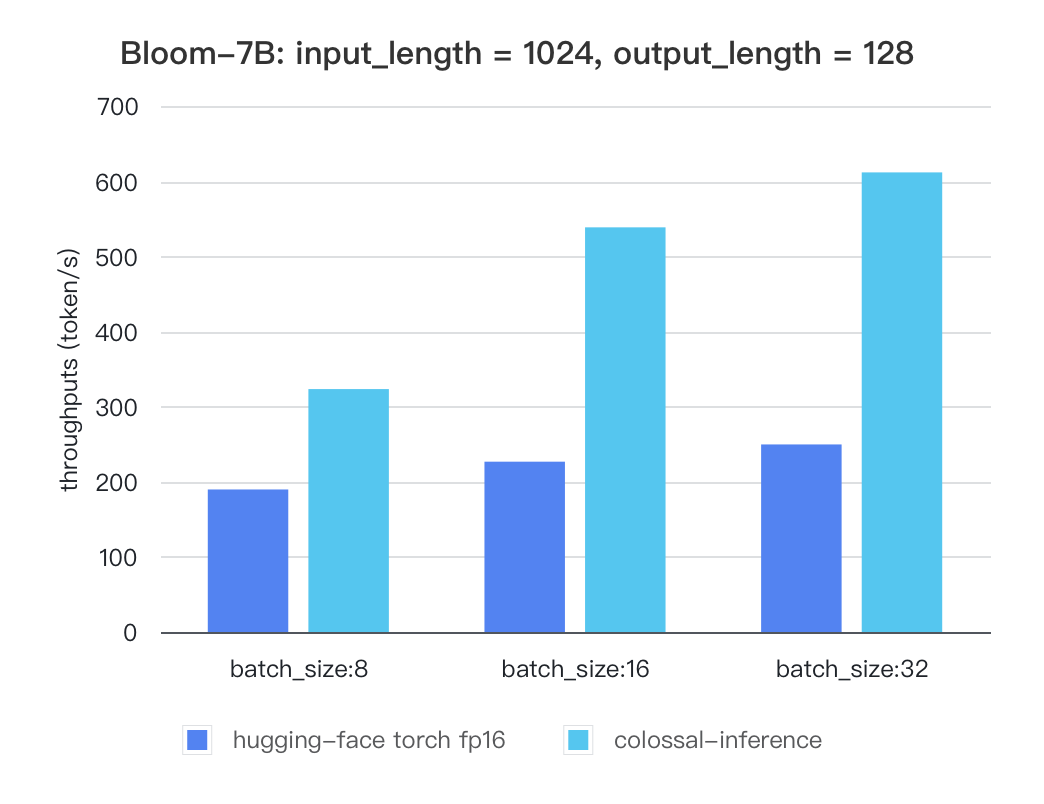
Currently the stats below are calculated based on A100 (single GPU), and we calculate token latency based on average values of context-forward and decoding forward process, which means we combine both of processes to calculate token generation times. We are actively developing new features and methods to further optimize the performance of LLM models. Please stay tuned.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Llama
|
||||
### Tensor Parallelism Inference
|
||||
|
||||
##### Llama
|
||||
|
||||
| batch_size | 8 | 16 | 32 |
|
||||
| :---------------------: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
|
||||
|
|
@ -131,7 +193,7 @@ Currently the stats below are calculated based on A100 (single GPU), and we calc
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Bloom
|
||||
#### Bloom
|
||||
|
||||
| batch_size | 8 | 16 | 32 |
|
||||
| :---------------------: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
|
||||
|
|
@ -140,4 +202,50 @@ Currently the stats below are calculated based on A100 (single GPU), and we calc
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Pipline Parallelism Inference
|
||||
We conducted multiple benchmark tests to evaluate the performance. We compared the inference `latency` and `throughputs` between `Pipeline Inference` and `hugging face` pipeline. The test environment is 2 * A10, 20G / 2 * A800, 80G. We set input length=1024, output length=128.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
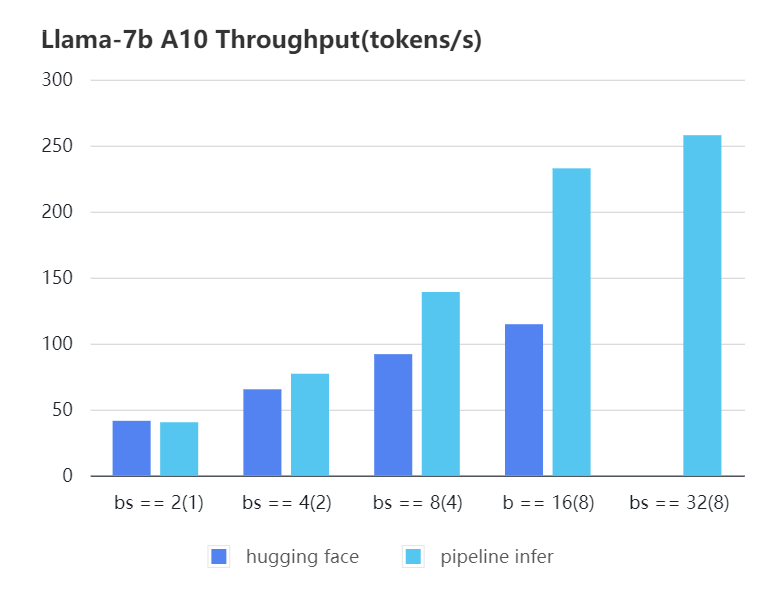
#### A10 7b, fp16
|
||||
|
||||
| batch_size(micro_batch size)| 2(1) | 4(2) | 8(4) | 16(8) | 32(8) | 32(16)|
|
||||
| :-------------------------: | :---: | :---:| :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: |
|
||||
| Pipeline Inference | 40.35 | 77.10| 139.03| 232.70| 257.81| OOM |
|
||||
| Hugging Face | 41.43 | 65.30| 91.93 | 114.62| OOM | OOM |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
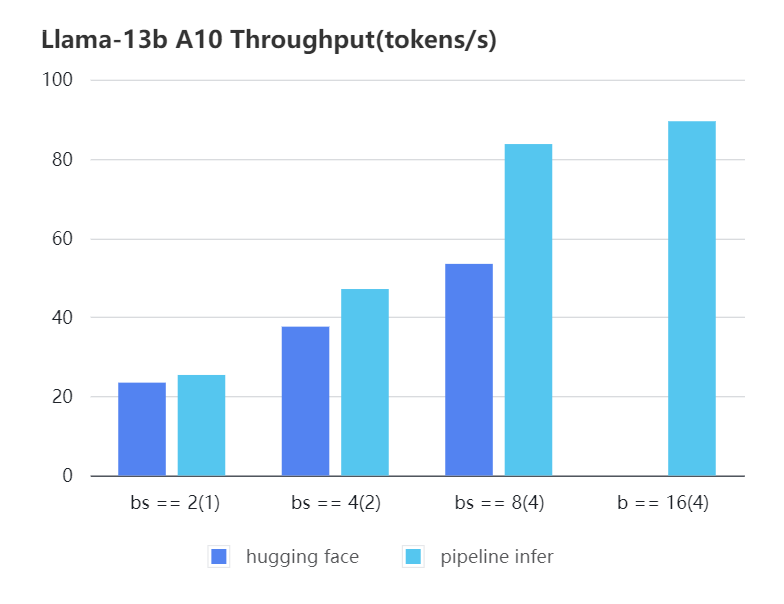
#### A10 13b, fp16
|
||||
|
||||
| batch_size(micro_batch size)| 2(1) | 4(2) | 8(4) | 16(4) |
|
||||
| :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: |
|
||||
| Pipeline Inference | 25.39 | 47.09 | 83.7 | 89.46 |
|
||||
| Hugging Face | 23.48 | 37.59 | 53.44 | OOM |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
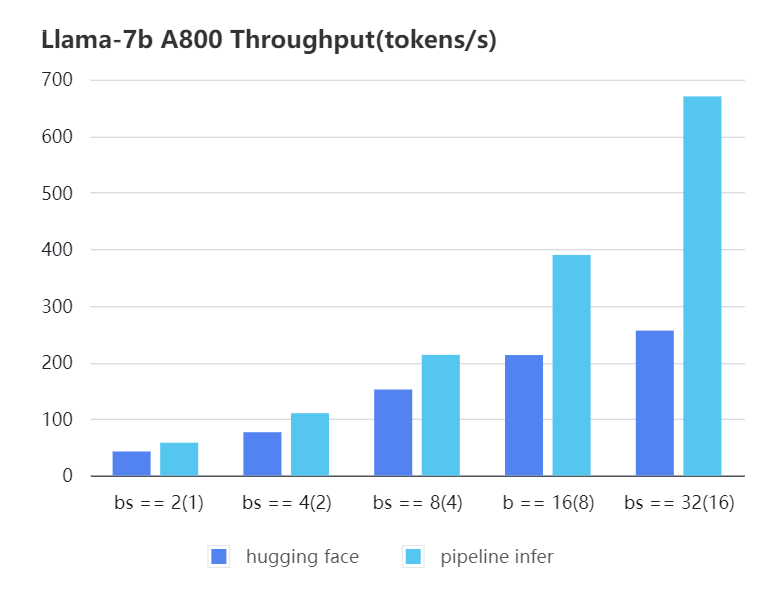
#### A800 7b, fp16
|
||||
|
||||
| batch_size(micro_batch size) | 2(1) | 4(2) | 8(4) | 16(8) | 32(16) |
|
||||
| :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: |
|
||||
| Pipeline Inference| 57.97 | 110.13 | 213.33 | 389.86 | 670.12 |
|
||||
| Hugging Face | 42.44 | 76.5 | 151.97 | 212.88 | 256.13 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
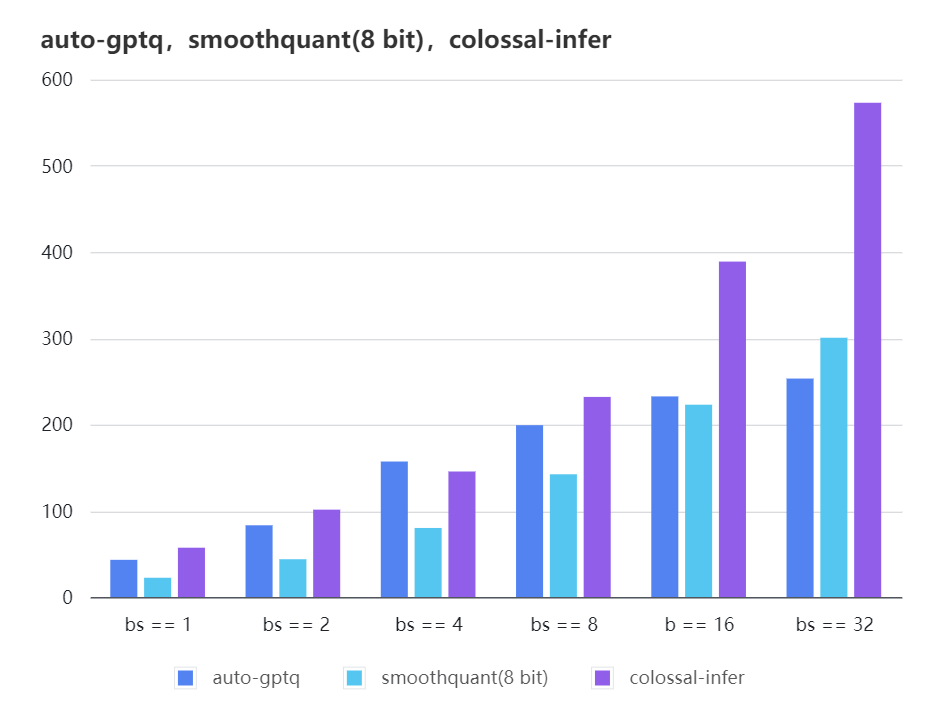
### Quantization LLama
|
||||
|
||||
| batch_size | 8 | 16 | 32 |
|
||||
| :---------------------: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
|
||||
| auto-gptq | 199.20 | 232.56 | 253.26 |
|
||||
| smooth-quant | 142.28 | 222.96 | 300.59 |
|
||||
| colossal-gptq | 231.98 | 388.87 | 573.03 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The results of more models are coming soon!
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue